- git
- how it began
- Django and model design
- how to run
- GCS roadmap
- development process
- hardware overview
- project overview
- streaming and frontend page
- Big picture and Environment Setup
- Video Streaming
- Drone Control Center
- Index Page
- Index Page Backend Endpoint
- Javascript Usages
- Js App initialization
- Updating System Data
- Drone Info DTO Definition
- Loading Drones Data
- Js Frontend Drone Abstraction
- Js Adding a Position marker to Drone Object
- Js Drone Controls Initializers and Keyboard Control Events Reader
- Js Rendering Map PointData Component
- UI Components Library Completion
- CSS - adding styles
- Update System Endpoint with Mock Data
- Demonstration - Mission/Command Endpoints + Frontend App
- Handler Manager Setup
- Adding Video Stream to UI Controls Page
- Rest Controller Functionality Implementation
- ControlManager Server Socket Connection Listener
- DroneHandler Initialization
- DroneHandler Network Message Sender and Receiver Threads
- DroneHandler Reading Latest Drone Data
- Protobuf Librarires Compilation
- DataMapper Transforming Protobuf Object to Domain Logic Objects
- Implementing Network Messaging Protocol
- Backend Application Build and Demonstration
- Prototype Build and Completion
- Distributed App Demonstration with two drones
- Feature Setup (chatbot)
- Weather API
- UI Unity application
- JDlab
- Drone-identification ISO
- Dron ID research pdf
git
- dashboard
deploy [email protected]:aiegoo/fcnd-heroku (fetch)
deploy [email protected]:aiegoo/fcnd-heroku (push)
heroku https://git.heroku.com/motion-planning.git (fetch)
heroku https://git.heroku.com/motion-planning.git (push)
origin https://eggs.or.kr/root/px4-autopilot.git (fetch)
origin https://eggs.or.kr/root/px4-autopilot.git (push)-
frontend
-
backend
-
webapp
-
git log
Click to open
- 676d54c (HEAD -> master, deploy/master)(2021-05-29) may29 mp4 testing
- 72f2258 (origin/master, origin/HEAD)(2021-02-18) timeseries visualization and datatable added
- b90aa24(2021-02-11) changed markers+lines to markers only
- dbd33e9(2021-02-11) added asyncio and done little text filtering
- 5e1df75(2021-02-11) session deletion added on frontend
- 9855640(2021-02-10) import missing icons
- 1cac94c(2021-02-10) added delete session and added waypoints path on map
- 255408d(2021-02-09) added models to admin and open vue views if no route found on django
- 90bd653(2021-02-09) added base map and start and goal position on map
- a2cf67f(2021-02-08) displaying the default base graph
- 25ea168(2021-02-08) getting sessions data in home only and added setMapData route
- 68204a1(2021-02-07) added start and goal of simulation
- e13faf4(2021-02-07) modified serializers and views | * 20ca848 (origin/hsyyu)(2021-02-07) create .env and edit backend/settings/dev.py |/
- 3334974(2021-02-06) adding sessions to home
- 70f895e(2021-02-06) added vuetify
- 47e58a6(2021-02-06) added timestamp to session and fixed typos
- c73d394(2021-02-06) getting session data
- 8f7b93d(2021-02-05) added some routes |\ | * 90cf892(2021-02-05) fixed latest()
-
679015a(2021-02-05) fixed latest() / - 225197b(2021-02-05) added serializers and api endpoints
- 6724daa(2021-02-04) added missing import
- 776629d(2021-02-04) added postgres for dev environment
- 8acebf3(2021-02-04) created some database models
- ee864e3(2021-02-04) Initial commit
how it began
This wiki is to refresh my memory and get it started with one of my client’s drone project. My project then was to create a dashboard with Django backend and Vue front-end to connect drone’s waypoints in real-time and display them on a map. Fortunately, both projects are relevant in many ways, except that mine used FCND simulator and waypoints and movements of drones were simulated inside a Unity app instead of open-source Mavlink/Simulink or even Ardupilot including QGroundControl. So here’s how the dashboard was built almost one year ago.
Be a copycat! Break someone else’s code.
Django and model design
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.postgres.fields import ArrayField
from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _
class Session(models.Model):
target_altitude = models.IntegerField("Target Altitude")
safety_distance = models.IntegerField("Safety Distance", default=5)
start = ArrayField(models.FloatField(), null=True)
goal = ArrayField(models.FloatField(), null=True)
is_finished = models.BooleanField("Is Finished", default=False)
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
class Meta:
verbose_name = _('Session')
verbose_name_plural = _('Sessions')
db_table = "session"
class Movement(models.Model):
session = models.ForeignKey(Session, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
timestamp = models.DateTimeField(auto_now=True)
value = ArrayField(models.FloatField())
class Meta:
get_latest_by = 'id'
verbose_name = _("Movement")
verbose_name_plural = _("Movements")
db_table = "movement"
class DroneData(models.Model):
session = models.ForeignKey(Session, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
timestamp = models.DateTimeField(auto_now=True)
local_position = ArrayField(models.FloatField())
local_velocity = ArrayField(models.FloatField())
global_position = ArrayField(models.FloatField())
global_home = ArrayField(models.FloatField())
class Meta:
get_latest_by = 'id'
verbose_name = _("Drone Data")
verbose_name_plural = _("Drone Datas")
db_table = "drone_data"
how to run
| django-vue |
 |
| fcnd-kalman |
 |
| unity-simulator |
 |
| simul-control keys |
 |
| how to npm to sync with browser |
  |
GCS roadmap
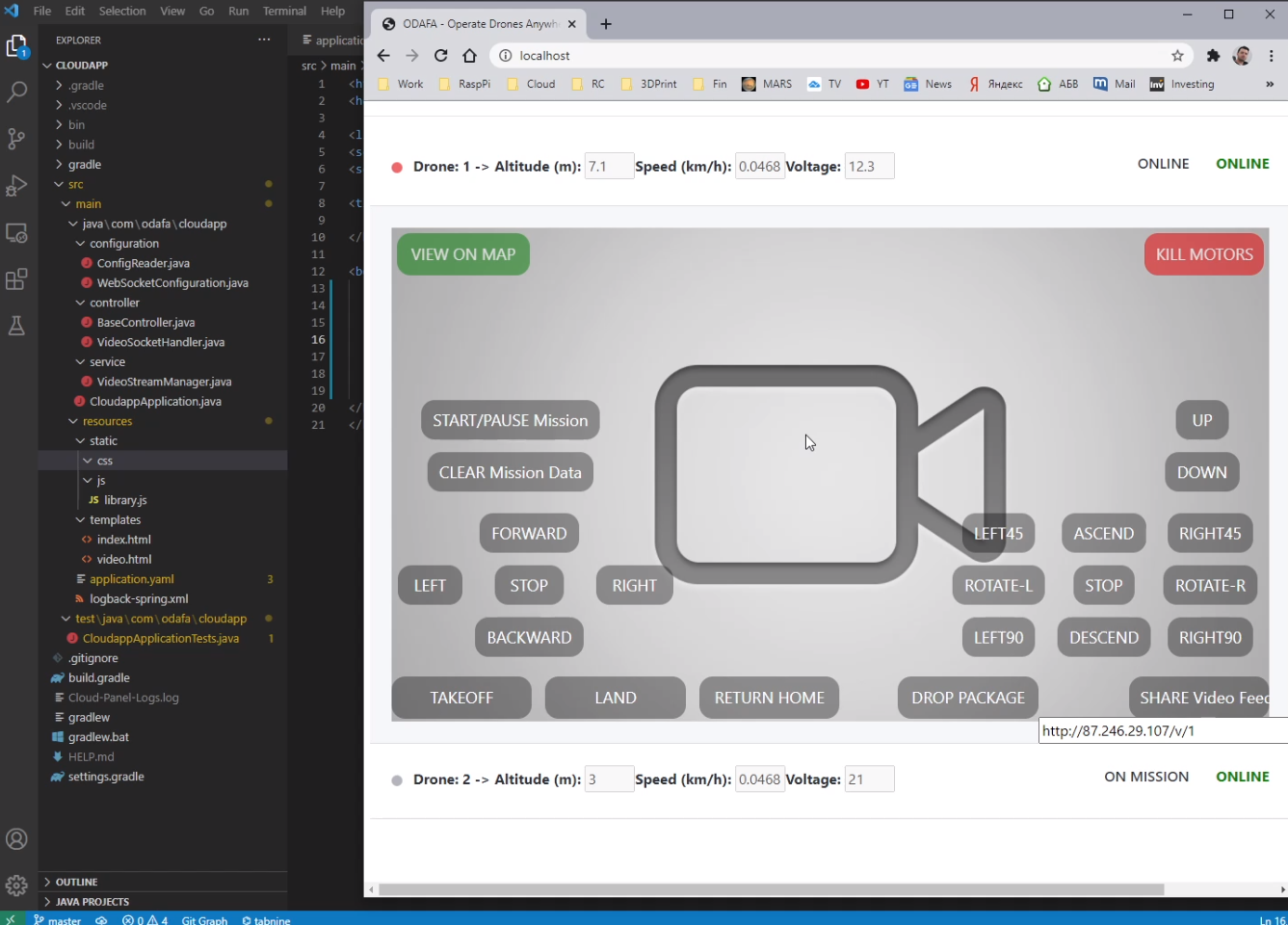
GCS overview (by lynx)
VTOL is an autonomous unmanned aircraft (drone) and capable of performing a mission from takeoff to landing without any intervention. It is highly advised that you still monitor the aircraft during the entire flight. The GCS receives live updates regarding the aircraft through the telemetry radio. You may change flight modes or intervene with the mission while flying. Uploading a new mission(s) or modifying an existing mission in flight is also possible.
The GCS is comprised of the following distinct sections.
Tab Selection
Used to select which tab you are on, each with a particular function. There are five tabs: Checklist, Plan, Geo-Tag, Parameters, and Settings.
Checklist: The Checklist tab is used to perform a preflight on your VTOL prior to every takeoff.
Plan: The Plan tab is used add waypoints, survey grids, actions, or rally points to your mission. The Plan tab is utilized during the preflight process but can also be used to modify a mission in flight.
Geo-Tag: The Geo-Tag menu is used to geo-reference images for mapping applications that do not require high accuracy. For post-processed kinematics (PPK) tagging, the standalone GeoTagz software is used. Geotagz is included with VTOL with the PPK option.
Parameters: The Parameters Tab is an used to modify and update parameters on the autopilot. Parameters are only to be changed if instructed to do so by SRP Aero support.
Settings: The Settings tab is used to configure GCS, equipment, and autopilot settings. The settings tab is also used to update firmware and license keys.
Side Menu
The side menu corresponds to what tab you are on.
Click to open
Menu Buttons
Each menu has unique buttons that change depending on which tab you are on. The very top button is used to collapse or expand the entire side menu. This can be useful when you are flying as it increases the overall map area. Top Status Bar
Displays important aircraft information.
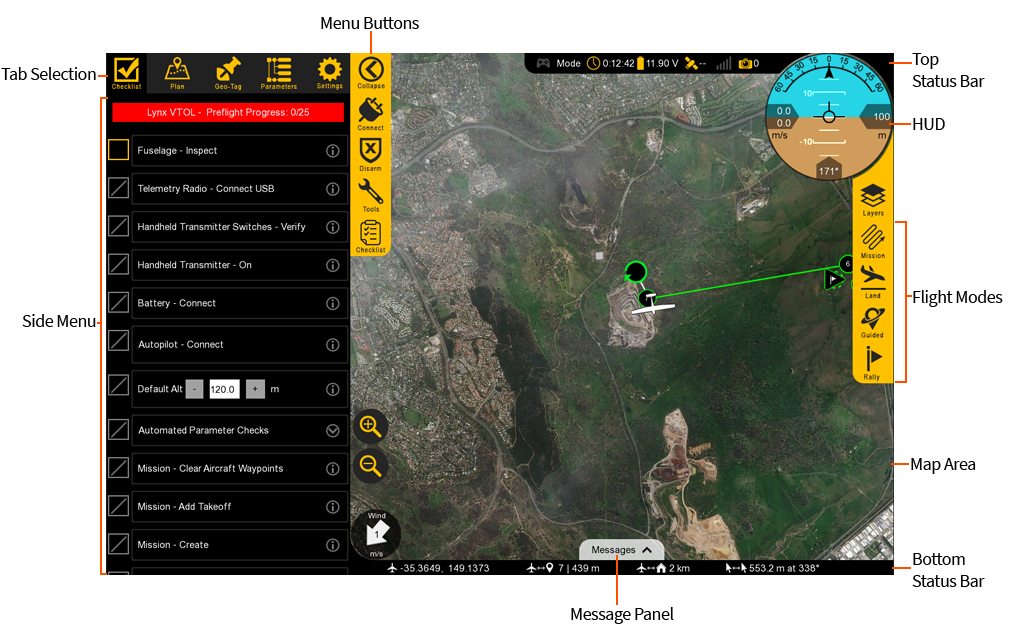
Gamepad: Indicates if a gamepad is connected to Swift GCS. This connection may be USB or Bluetooth. Swift GCS only recognizes XBox controllers. Note, this functionality is not fully supported at this time.
Mode: Displays the current flight mode.
Timer: Displays the current flight in Hours:Minutes:Seconds. The timer automatically starts on takeoff and stops when the aircraft lands and disarms. The aircraft must be restarted (turned off and on) to reset the timer.
Battery: Displays the main battery voltage. Click on the battery icon to expand this menu. The VTOL battery voltage is displayed in the expanded menu.
GPS: Displays the GPS and GNSS satellite count.
Telemetry: Displays the telemetry radio’s signal strength.
Camera: The camera icon displays photo count for cameras equipped with feedback. Feedback is essential for PPK tagging but is also helpful to see if and when the camera is taking photos.
:::
Flight Modes
Used to change modes and aircraft location.
Map: The Map menu is used to configure how the aircraft icon and waypoints are displayed on the map. Under this menu is also where you can toggle the terrain view and load KML overlays.
Mission: In the mission menu, you can change the flight mode to Auto, restart the mission, or select an individual item in your mission to fly to.
Land: Select land to begin your planned landing or to execute an emergency landing.
Guided: The Guided flight mode is a 'fly here' mode. In Guided, you choose a spot on the map that the aircraft flies to and circles.
Rally: The Rally flight mode is automatically used when the aircraft completes its mission or a failsafe activates. You can also select the Rally flight mode. In this flight mode, the aircraft will navigate to the nearest Rally point and circle.
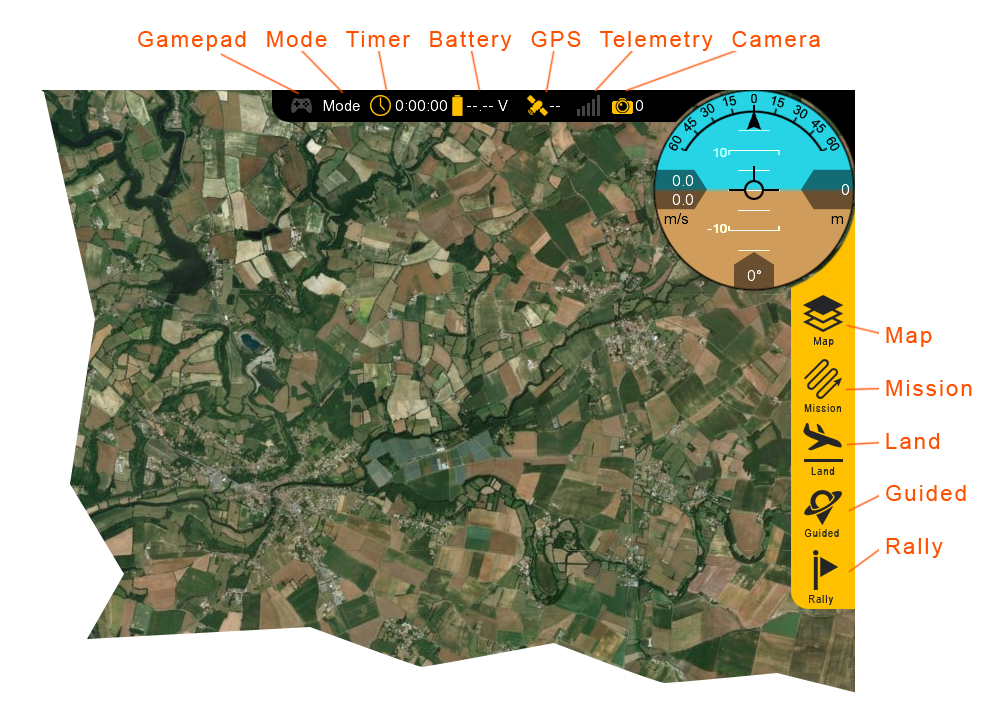
Bottom Status Bar
Displays aircraft location and waypoint information.
Click to open
Zoom in/Out: Zooms the map area in or out. On touchscreen devices, you can also use ‘pinch-zoom’.
Wind: Displays the wind velocity and direction that the wind is blowing.
Aircraft Location: Current aircraft location coordinates shown in decimal degrees format.
Next Waypoint: Displays the next waypoint number in your mission and the distance to that waypoint from the aircraft.
Messages: The message panel displays warnings and notifications from the GCS and autopilot. A new warning will automatically expand the message panel if it was collapsed.
Home: Shows the distance from the aircraft to home. If you have a tablet with built-in GPS, this can be toggled to show the distance from the aircraft to your location.
Click Distance: Click distance shows the distance between your last two mouse clicks. This is a quick and useful tool for planning purposes such as determining how far away something is on the map. :::
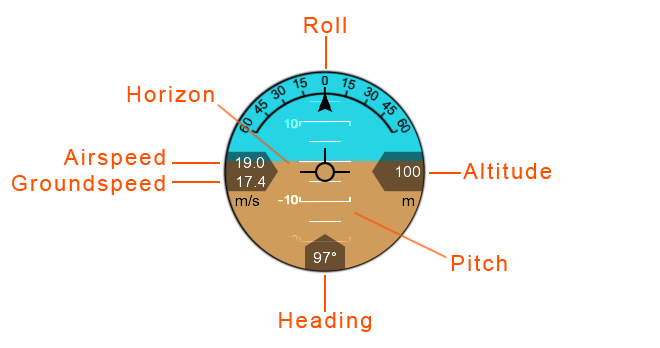
HUD
The Heads-Up Display (HUD) displays aircraft information and attitude against a horizon line.
Roll: The aircraft’s roll in degrees (bank angle).
Altitude: The aircraft’s altitude above the ground. The unit is displayed below the altitude reading.
Pitch: The aircraft’s pitch in degrees.
Heading: The aircraft’s magnetic heading.
Horizon: The aircraft’s attitude is shown against an artificial horizon.
Ground Speed: The speed of the aircraft relative to the ground. The unit for both ground and airspeed is displayed below.
Airspeed: The speed of the aircraft relative to the air through which it is moving.
Map Area
The Map displays the background satellite imagery with the position of aircraft flying over it. Currently there are two sources of map imagery: Mapbox and ESRI. The map area is also where your mission items and polygons will be shown.
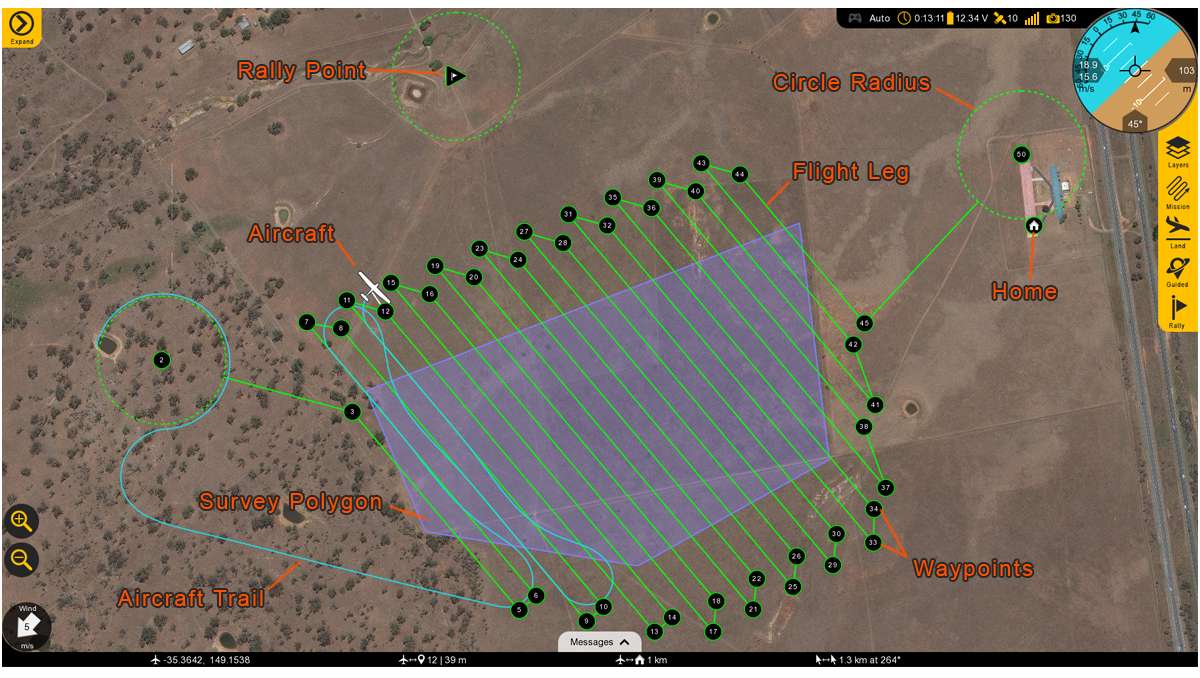
Rally Point: The Rally icon shows the location of your planned Rally points. The icon is a flag within a triangle.
Click to open
Flight Leg: The flight legs connect each waypoint in sequence. They are an approximate indication of how the aircraft will fly from one waypoint to the next. They do no account for the turning radius of the aircraft. It is normal to observe small deviations from the flight legs in windy conditions.
Circle Radius: A dashed line will appear around certain waypoints that have a radius. Examples include the landing pattern and loiters.
Home: Displays the home location. Home is your takeoff location.
Waypoints: Displays the location of your planned waypoints. Each waypoint is numbered. Waypoints are used to fly to a location in the sky. The aircraft will fly through or near the waypoint and then proceed to the next item in your mission. Waypoints are automatically generated when creating a survey.
Survey Polygon: A survey polygon displays the area on the ground that you are mapping. Survey polygons are created from the Plan tab ⇨ Survey. You can draw a new region or load a KML or KMZ (Google Earth format). Flight legs will extend past the polygon area to account for the extra space that the aircraft needs to turn around. Viewing the polygon can be toggled on/off from the Map button ⇨ Survey. Multiple survey areas can be planned into your mission.
Aircraft Trail: The aircraft trail shows the history of the aircraft’s flight path. At a certain length, the trail will automatically begin to disappear. The trail can also be clear manually from the Map button ⇨ Clear Aircraft Trail.
Aircraft: Displays the aircraft location and heading.
:::


DTO(data transfer format) is defined as drone_id, longitude, latitude, battery, state, altitude and speed
public class DroneInfo {
private final String id;
private final double lattitude;
private final double longitude;
private final double speed;
private final double alt;
private final double battery;
private final String state;
}
| Field | Required Value |
|---|---|
| command | MAV_CMD_NAV_VTOL_TAKEOFF |
| frame | MAV_FRAME_GLOBAL_RELATIVE_ALT |
| x | 0 |
| y | 0 |
| z | Altitude above home to takeoff to in meters |
- landing
A VTOL landing consists of a number of waypoints. If these are not all planned as specified then the aircraft may be unable to perform failsafes, or may encounter terrain obstructions while flying the landing. The waypoints must be planned as specified below.
Click to open
| Field | Required Value |
|---|---|
| command | MAV_CMD_DO_LAND_START |
| x | Landing latitude in degrees * 107 |
| y | Landing longitude in degrees * 107 |
| Field | Required Value |
|---|---|
| command | MAV_CMD_NAV_LOITER_TIME |
| param1 | 1 |
| x | Landing latitude in degrees * 107 |
| y | Landing longitude in degrees * 107 |
| z | Approach altitude in meters (can be relative or global height according to the frame field) |
| Field | Required Value |
|---|---|
| command | MAV_CMD_NAV_LOITER_TO_ALT |
| x | Landing latitude in degrees * 107 |
| y | Landing longitude in degrees * 107 |
| z | Approach altitude in meters (can be relative or global height according to the frame field) |
| Field | Required Value |
|---|---|
| command | MAV_CMD_NAV_VTOL_LAND |
| frame | MAV_FRAME_GLOBAL_RELATIVE_ALT |
| x | Landing latitude in degrees * 107 |
| y | Landing longitude in degrees * 107 |
| z | Transition altitude (above home) in meters |
Once armed, the aircraft will takeoff vertically and transition to forward flight. doc
- forward flight mode comparison
| Forward Modes | Auto | Rally | Guided | Cruise | FBWB | Manual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interface | GCS | GCS | GCS | Controller | Controller | Controller |
| Link | Telem | Telem | Telem | RC | RC | RC |
| Controlled by | Mission | Rally Point | Guided Point | Sticks | Sticks | Sticks |
| Autonomous | x | x | x | |||
| Stabilized Pilot Inputs | x | x | ||||
| GPS Required | x | x | x | x | ||
| Ground Track | x | x | x | x |
- vertical flight mode comparisons
| Vertical Modes | Auto | QLand | QLoiter | QStabilize |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interface | GCS | Controller | Controller | Controller |
| Link | Telem | RC | RC | RC |
| Controlled by | Mission | Sticks | Sticks | Sticks |
| Autonomous | x | x | ||
| GPS Required | x | x | x | |
| Stick Nudging | x | |||
| Weathervaning | x | x | x | |
| Forward Assist | x | x | x |
:::
Flying category
- Mission planning
- Changing flight modes
- Available flight mode
- Data links
- Reconnecting in flight
- failsafe
- warnings / arming warnings
development process
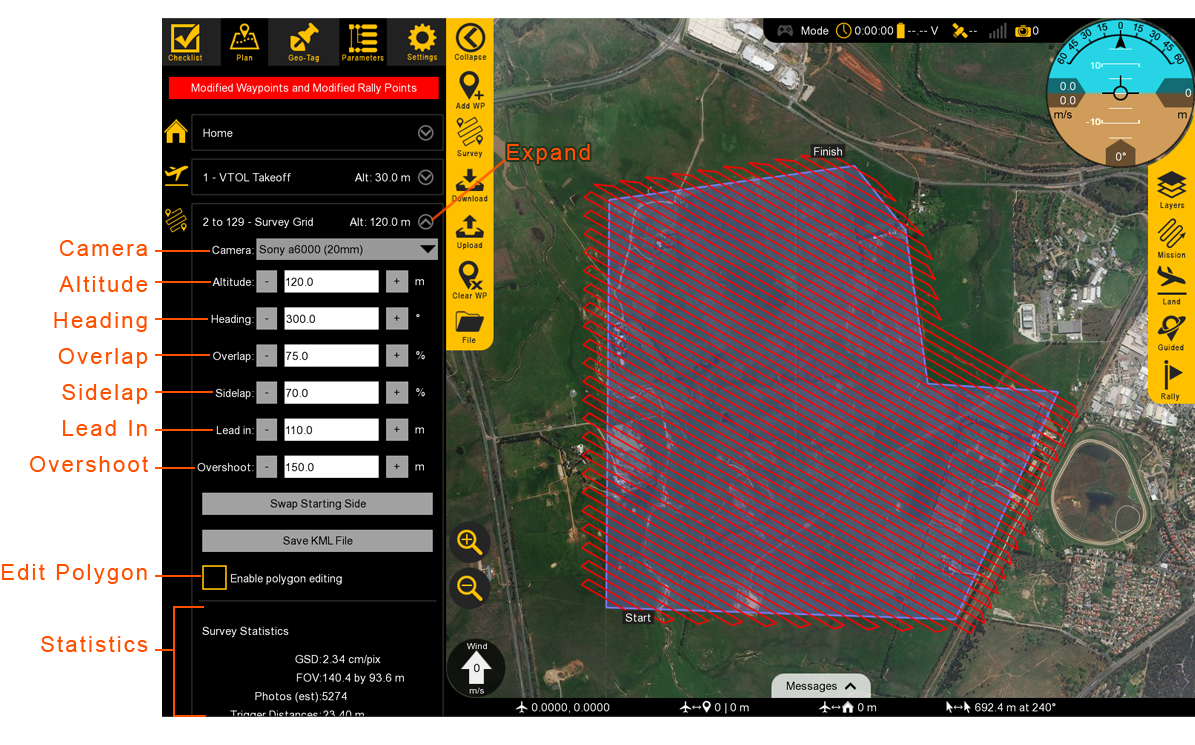
The following milestones include only developer’s steps for external sharing. Actual itinerary will occur concurrently for the relevant process and workloads as his development progresses. For example, the front-end page and Django db setup will start from the earlier stage, as well as adding styles to the UI/UX would too.
Some of the technologies in pursuing this routes are assumed ‘not tested’, which means changes are highly likely to follow, affecting schedule and sourcing out of all proposed components such as time, a necessity to outsource, or UI designs. One example of this would be ‘video streaming’ and network infrastructure for latency and concurrency. Please read my other wiki mqtt_websocket for options and issues raised by woowahan teams.
goals:
- Build Low Latency Cloud App to Operate From Anywhere in the World
- How to Control Drone with Python Application running on a Raspberry Pi
- Connecting Multiple Python Applications to a Single Remote App
- Managing Data Concurrently from Many Python Applications
- Low Latency Video Streaming from Raspberry Pi to a Web Page
- How to Have Many Active Video Streams on a Single Web Page
- Buiding a spa with javascript
- How to Control Simultaneously Many Drones From a Single Web Page
- Using Google Maps API to Setup and Read Mission Data From a User
- Real Time Data Visualization From the Drones on the Interactive Map
- Use Framework MVC to build Application For 4G Drone Control
- Multithreading Application Design
- Multithreading Application Design in Python
- Distributed Application Design
- Python Dronekit Library for MavLink Communication with Autopilot
- More feature components below as discussed
Main UI components
Checklist, Plan, Geo-Tag(geo-fence), Parameters(controls), Video-streaming(wowza, window media streaming, on webrtc) and Settings
Feature components
Chatbot, Log Analysis, Network , Status Bar and Weather API
project management
Pivotal, Googlesheet, Github Projects, Jira, or other options
required infra
Drone sensors, api/db/web servers, cloud computing resources
software platform
Front/back-end, database, OS(Ubuntu, rapibe)
issues tracker
브로드 캐스팅 cron job을 사용하여 2분에 1번씩 batch proccess 한곳에서 만 배달 데이터를 select 하여 database 부하를 줄이면서socket.io 실시간 이벤트로 브로드캐스팅을 하도록 하고 client는 수신받은 데이터로 유실이 발생한 배달 리스트를 fetch 하는 것으로 이벤트 누락에 대한 데이터 미변경을 보완 하였고 적용 이후에는 데이터 미변경에 대한 문제가 보고 되지 않았습니다
hardware overview
link hardware-setup
project overview
- Key technology:
- logging/user database to be used for api calls
- video streaming latency and concurrency handler
- Monolithic or distributed architectures
- Microservice and modular applications
- visualization of logging, mission and weather apis
- messaging or chatbot features
- PA broadcasting features
- user admin for permission levels and accessibility
- How progress is scheduled
note demo sessions are scheduled as indicated in blue color.
| Documentation | DIY drone hardware overview |
| Video steaming and front-end control | Environment setup |
| Raspi hardware/network setup | * initial app layout |
| * logging setup async | Python initial app layout |
| raspi as linux service | Configuration reader setup |
| video streaming app | Html video page |
| js video stream client | * home controller video endpoint |
| * configuration reader | * web-socket config |
| * Video stream manager | App overview demo |
| Drone control center html | * backend endpoint |
| js usage | js app initialization |
| js update system data | * drone info dto |
| Js loading drone data | js frontend drone abstraction |
| js adding a position marker | Js drone control intializer keyboard mapping |
| js rendering map point | Js UI component lib |
| css | * update system endpoint with mock data |
| * mission command end point | Js adding video stream to ui control |
| * rest controller functionality | * control manager server socket |
| * dronehandler init | * dronehanlder network message sd/rv thread |
| * droneHandler reading latest data | Prbf* |
| * datamapper transforming protobuf object to domain logic objects | |
| * implementing network messaging protocol | * backend application |
| * backend application | Python overview |
| Python bootsrapiproject overviewng initial app | Python Network connection monitoring |
| Python data receiver thread | Python drone object vehicle abstraction |
| Python network messages encoding | Python drone control panel object |
| Python maintaining constant speed and direction | Python camera serve controlling thread |
| Python camera server control | Python finished application logic |
| Final result full distributed application | realworld flight demo |
streaming and frontend page
- current front-end filesystem
| filesystem | ⬌ | filesystem |
|---|---|---|
.
├── css
│ ├── home.css
│ └── login.css
├── home.html
├── images
│ └── drone-icon2.png
├── index.html
└── js
├── home.js
├── index.js
├── jsmpeg.min.js
├── map.js
├── mqtt.js
├── mqttws31.js
└── mqttws31-min.js
|
future filesystem | |
.
├──cloudapp
│ ├── CloudappApplication
│ ├── configuration
│ │ ├── ConfigReader
│ │ └── WebSocketConfiguration
│ ├── controller
│ │ ├── BaseController
│ │ ├── BaseRestController
│ │ └── VideoSocketHandler
│ ├── dto
│ │ ├── DataPoint
│ │ └── DroneInfo
│ ├── service
│ │ ├── ControlManager
│ │ ├── DroneHandler
│ │ └── VideoStreamManager
│ └── utils
│ ├── DataMapper.java
│ ├── NetworkFormatter
│ └── ProtoData.
└── resourcesproject overview
├── application.yaml
├── logback
├── protobuf
├── static
│ ├── css
│ │ └── app.css
│ ├── drone.svg
│ ├── js
│ │ ├── app.js
│ │ ├── library.js
│ │ └── ui-components
│ └── video.jpg
└── templates
├── index.html
└── video.html
|
modular |
Big picture and Environment Setup
sudo -H pip install dronekit=2.9.1
Initial Dependencies:
sudo apt-get install python-dev python-opencv
python-wxgtk3.0 python-matplotlib python-pygame
python-lxml python-yaml vim git
sudo apt install python-pip
pip --version (make sure its working)
sudo pip install --upgrade pip
pip --version (make sure its working)
sudo pip install MAVProxy==1.6.2
sudo usermod -a -G dialout $USER
sudo apt-get remove modemmanager
Raspi plus Hardware and Network setup
Initial App layout - libraries
Logging Setup - Async Logback
Python Initial App Layout
Video Streaming
Python Setup on raspi as a linux service
Configuration Reader Setup
Basic Video Streaming Setup
@GetMapping("/")
public String indexPage(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("publicIp", getPublicIpAddress());
model.addAttribute("defaultSpeed", configurations.getDefaultSpeed());
model.addAttribute("defaultAltitude", configurations.getDefaultAltitude());
model.addAttribute("videoEndpoint", configurations.getVideoWsEndpoint());
return "index";
}
Video Page
Video Stream Client
class Drone {
constructor(id, lat, lng) {
this.id = id;
this.lat = lat;
this.lng = lng;
this.videoSocket = new VideoStreamClient(id, PUBLIC_IP, 80, VIDEO_ENDPOINT);
this.posMark = new google.maps.Marker({
position: { lat: lat, lng: lng },
map: WORLD_MAP,
label: id + '',
icon: 'drone.svg'
});
this.locationToPointDataMap = new Map();
this.labelCounter = 0;
this.speed = 0.0;
this.alt = 0.0
}
Home Comptroller Video Endpoint
Configurations Reader
Websocket Configuration
Video Stream manager
Demonstration
Drone Control Center
Index Page
Index Page Backend Endpoint
Javascript Usages
Js App initialization
Updating System Data
Drone Info DTO Definition
Loading Drones Data
Js Frontend Drone Abstraction
Js Adding a Position marker to Drone Object
Js Drone Controls Initializers and Keyboard Control Events Reader
Js Rendering Map PointData Component
UI Components Library Completion
CSS - adding styles
Update System Endpoint with Mock Data
Demonstration - Mission/Command Endpoints + Frontend App
Handler Manager Setup
Adding Video Stream to UI Controls Page
Rest Controller Functionality Implementation
ControlManager Server Socket Connection Listener
DroneHandler Initialization
DroneHandler Network Message Sender and Receiver Threads
DroneHandler Reading Latest Drone Data
Protobuf Librarires Compilation
DataMapper Transforming Protobuf Object to Domain Logic Objects
Implementing Network Messaging Protocol
Backend Application Build and Demonstration
Prototype Build and Completion
Network Connection Monitoring Thread
Data Receiver Thread
Drone Object Vehicle Abstraction
Network Message Encoding-Decoding Layer
Drone Control Panel Object
Maintaing Constant Speed and Direction Thread
Camera Servo Controlling Thread
Logic Flow Overview
Distributed App Demonstration with two drones
Feature Setup (chatbot)
Weather API



The surface analysis chart depicts an analysis of the current surface weather. [Figure 13-10] This chart is transmitted every 3 hours and covers the contiguous 48 states and adjacent areas. A surface analysis chart shows the areas of high and low pressure, fronts, temperatures, dew points, wind directions and speeds, local weather, and visual obstructions. Surface weather observations for reporting points across the United States are also depicted on this chart. Each of these reporting points is illustrated by a station model. [Figure 13-11] A station model includes:
• Sky cover—the station model depicts total sky cover and is shown as clear, scattered, broken, overcast, or obscured/partially obscured.
• Sea level pressure—given in three digits to the nearest tenth of a millibar (mb). For 1,000 mbs or greater, prefix a 10 to the three digits. For less than 1,000 mbs, prefix a 9 to the three digits.
• Pressure change/tendency—pressure change in tenths of mb over the past 3 hours. This is depicted directly below the sea level pressure.
• Dew point—given in degrees Fahrenheit.
• Present weather—over 100 different standard weather symbols are used to describe the current weather.
• Temperature—given in degrees Fahrenheit.
• Wind—true direction of wind is given by the wind pointer line, indicating the direction from which the wind is blowing. A short barb is equal to 5 knots of wind, a long barb is equal to 10 knots of wind, and a pennant is equal to 50 knots.
UI Unity application









visual flight rules (VFR) or IFR, aircraft identification and type, departure point, estimated time of departure (ETD), flight altitude, route of flight, destination, and estimated time en route (ETE).
JDlab

 UAM is considered a subset of advanced air mobility (AAM).1213 AAM provides local, regional, and intraregional service in addition to the urban service of UAM, with intra- and inter-city transport and an expected 50–300 mile maximum range, respectively. NASA is a key AAM pioneer whose extensive AAM vision is depicted as in above.
UAM is considered a subset of advanced air mobility (AAM).1213 AAM provides local, regional, and intraregional service in addition to the urban service of UAM, with intra- and inter-city transport and an expected 50–300 mile maximum range, respectively. NASA is a key AAM pioneer whose extensive AAM vision is depicted as in above.
fixedwing
Drone-identification ISO

Dron ID research pdf
- usa
| 0 | • 드론과 조종자 간의 거리가 최대 122m(400ft) 이내 가시권 내 비행 •14 CFR Part 101 준수하는 드론(일부 제외) •ATC 관리하에 운영되는 드론 •FAA에 의해 식별 및 추적이 면제되는 드론 |
| 1 | •0 2 3 단계에 속하지 않는 드론 •14 CFR Part 107에 속하는 드론 |
| 2 | •비가시권 비행 드론 • 14 CFR Part 107에서 정의한 최대고도 이상에서비행하는 드론 • 보호되지 않는 사람에게 운영되는 드론 |
| 3 | • 무게가 25kg 이상이고 비가시권 내 비행하는 드론 • IFR 조건에서 동작하는 드론 • 통제된 공역에서 비행하는 드론 |
- EU
| CL0 | • 최대 이륙 중량 250g 이하 • 최대 비행 속도 19m/s 이하 • 최대 비행 고도 120m 이하 • 최대 허용 전압 24V • 드론 원격 식별 불필요 |
| CL1 | • 최대 이륙 중량 900g 이하(운동에너지 80J 이하) • 최대 비행 속도 19m/s 이하 • 최대 비행 고도 120m 이하 • 최대 허용 전압 24V • ANSI/CTA-2063 기반 시리얼 번호 • 드론 등록 및 원격 식별 필요 • 지형 인식 시스템 장착 • 라이트 설치 |
| CL2 | • 최대 이륙 중량 4kg 이하 • 최대 비행 고도 120m 이하 • 최대 허용 전압 48V • ANSI/CTA-2063 기반 시리얼 번호 • 드론 등록 및 원격 식별 필요 • 지형 인식 시스템 장착 • 라이트 설치 • 드론 제어 링크 통신 단절 시 통신 복구 기능 또는 안전한 비행 종료 기능 필요 |
| CL3 | • 최대 이륙 중량 25kg 이하 • 최대 비행 고도 120m 이하 • 최대 허용 전압 48V • ANSI/CTA-2063 기반 시리얼 번호 • 드론 등록 및 원격 식별 필요 • 지형 인식 시스템 장착 • 라이트 설치 • 드론 제어 링크 통신 단절 시 통신 복구 기능 또는 안전한 비행 종료 기능 필요 |
| CL4 | • 최대 이륙 중량 25kg 이하 • 최대 비행 고도 및 속도 제한 없음 |
The following wiki, pages and posts are tagged with
| Title | Type | Excerpt |
|---|---|---|
| webscraping | page | webscraping lessons, rapa, blackyak, 100 famous mountains, github actions and python install |
| project for LasVegas 2020 CES | portfolio | this project has been showcased by Mobis for CES 2020 |
| project for LasVegas 2020 CES | portfolio | the most advanced hardware and software ecosystem for enterprise drones |
