Overview
Machine Learning (ML) at the edge involves deploying ML models directly on edge devices, such as IoT devices, smartphones, cameras, and other embedded systems, instead of relying on centralized cloud servers. This approach offers several benefits, including reduced latency, improved privacy, and decreased bandwidth usage. Here are some key aspects and considerations for deploying ML at the edge:
Key Benefits
- Reduced Latency:
- Real-time processing on the device eliminates the need to send data to and from the cloud.
- Essential for applications like autonomous vehicles, real-time video analytics, and industrial automation.
- Improved Privacy and Security:
- Sensitive data is processed locally, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Compliance with data protection regulations is easier when data does not leave the device.
- Bandwidth Efficiency:
- Reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over networks, saving bandwidth and reducing costs.
- Beneficial for applications in remote areas with limited connectivity.
- Reliability:
- Edge devices can operate independently of network connectivity, ensuring continuous operation even when offline.
Challenges
- Resource Constraints:
- Edge devices often have limited computational power, memory, and storage compared to cloud servers.
- Requires optimization of ML models to run efficiently on constrained hardware.
- Deployment Complexity:
- Managing and updating models on a large number of distributed devices can be challenging.
- Requires robust deployment strategies and monitoring systems.
- Data Management:
- Handling data storage, processing, and security at the edge requires careful planning.
- Ensuring consistency and synchronization with cloud or central servers can be complex.
Techniques and Technologies
- Model Optimization:
- Quantization: Reducing the precision of model weights to lower bit-widths (e.g., 8-bit integers) to save memory and improve inference speed.
- Pruning: Removing less significant parts of the model to reduce its size and complexity without significantly impacting accuracy.
- Knowledge Distillation: Training a smaller, more efficient model (student) to mimic the behavior of a larger, more accurate model (teacher).
- Hardware Acceleration:
- Utilizing specialized hardware like GPUs, TPUs, or dedicated ML accelerators (e.g., Google Edge TPU, NVIDIA Jetson, Intel Movidius) to enhance performance.
- Leveraging FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) for custom hardware acceleration.
- Edge Frameworks and Platforms:
- TensorFlow Lite: A lightweight version of TensorFlow designed for mobile and embedded devices.
- ONNX Runtime: An optimized runtime for executing models in the Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX) format.
- AWS IoT Greengrass: Enables local compute, messaging, data caching, sync, and ML inference capabilities on connected devices.
- NVIDIA Jetson: A platform for AI at the edge, providing powerful development kits and pre-trained models.
- Data Processing and Management:
- Implementing local data preprocessing, feature extraction, and anomaly detection to reduce the amount of data needing to be processed by the ML model.
- Using local databases or lightweight data storage solutions to manage data efficiently on edge devices.
Use Cases
- Smart Home Devices:
- Voice assistants, security cameras, and smart thermostats that process data locally to provide fast and reliable responses.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT):
- Predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and anomaly detection in manufacturing and industrial environments.

- Healthcare:
- Wearable devices that monitor health metrics and provide instant feedback or alerts without needing continuous cloud connectivity.
- Autonomous Vehicles:
- Real-time perception, decision-making, and control systems that operate independently of cloud infrastructure.
- Retail:
- Smart checkout systems, customer behavior analysis, and inventory management using edge-based ML.
Additional Use Cases (KR + EN)
| 분류/목표 | 세부 프로그램 | 소요 시간 |
|---|---|---|
| 🧪 실험실 실험 실습 위험한 시약 없이 진행 |
일반물리: 운동량 충돌 실험 | 5분 |
| 일반화학: 아스피린 합성 | 5분 | |
| 재료역학: 인장시험 | 5분 | |
| 폐시약 폐기 (교육) | 5분 | |
| ⚠️ 산업 안전 사고 재현과 대처 훈련 |
시설관리: 전기 직무 체험 | 5분 |
| 시설관리: 기계 직무 체험 | 5분 | |
| 시설관리: 소방 직무 체험 | 5분 | |
| 🏠 생활/재난 안전 대피 구조 순서 훈련 |
화재 발생 즉시 대피 | 5분 |
| 지진 발생 즉시 대피 | 5분 | |
| ⚙️ 에스컬레이터 점검 교육 시설관리 체험 |
에스컬레이터 점검 교육 | 10분 |
| 🚶 물리치료 동작을 따라하며 재활 체험 |
물리치료: 근육과 근육 작용 | 10분 |
| 💻 반도체 공정 견학 클린룸 공정 가상 투어 |
반도체 8대 공정 견학 | 5분 |
한국어 원문
실험실 실험 실습 (위험한 시약없이 진행)
- 일반물리 운동량 출동 실험 (5분)
- 일반화학 아스피린 합성 (5분)
- 재료역학 인장시험 (5분)
- 폐시약 폐기 (5분)
산업안전 (사고 재현과 대처 훈련)
- 시설관리 전기 직무 체험 (5분)
- 시설관리 기계 직무 체험 (5분)
- 시설관리 소방 직무 체험 (5분)
생활/재난안전 (대피·구조 순서 훈련)
- 화재발생 즉시 대피 (5분)
- 지진발생 즉시 대피 (5분)
에스컬레이터 점검 교육 (시설관리 체험)
- 에스컬레이터 점검 교육 (10분)
물리치료 (동작을 따라하며 재활 체험)
- 물리치료 근육과 근육 작용 (10분)
반도체 공정 견학 (클린룸 공정 가상 투어)
- 반도체 8대 공정 견학 (5분)
English Translation
Laboratory Practice (Risk-free chemical simulation)
- Intro Physics: Momentum collision experiment (5m)
- General Chemistry: Aspirin synthesis simulation (5m)
- Strength of Materials: Tensile test (5m)
- Waste reagent disposal workflow (5m)
Industrial Safety (Incident recreation & response)
- Facilities (Electrical) task experience (5m)
- Facilities (Mechanical) task experience (5m)
- Facilities (Fire safety) task experience (5m)
Life / Disaster Safety (Evacuation & rescue sequence)
- Fire evacuation drill (5m)
- Earthquake evacuation drill (5m)
Escalator Inspection Training (Facilities)
- Escalator inspection course (10m)
Physical Therapy (Guided movement rehabilitation)
- Muscles & muscle action module (10m)
Semiconductor Process Virtual Tour
- 8 core semiconductor process walkthrough (5m)
Conclusion
ML at the edge is a powerful paradigm that brings advanced intelligence closer to where data is generated, enabling real-time, secure, and efficient processing. While it presents challenges, advancements in model optimization, specialized hardware, and edge computing frameworks are making it increasingly feasible. By carefully considering the benefits and challenges, and leveraging the appropriate technologies, businesses can harness the full potential of edge ML to drive innovation across various domains.
LLM Learning Curves and State-of-the-Art Projects
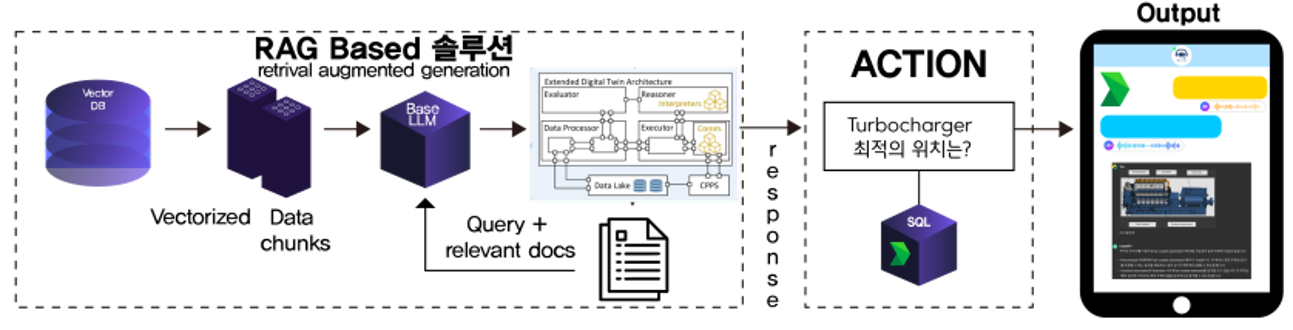
In addition to the exploration of ML at the edge, I have been working on various projects involving LLM models and RAG techniques. Here are some of the recent highlights:
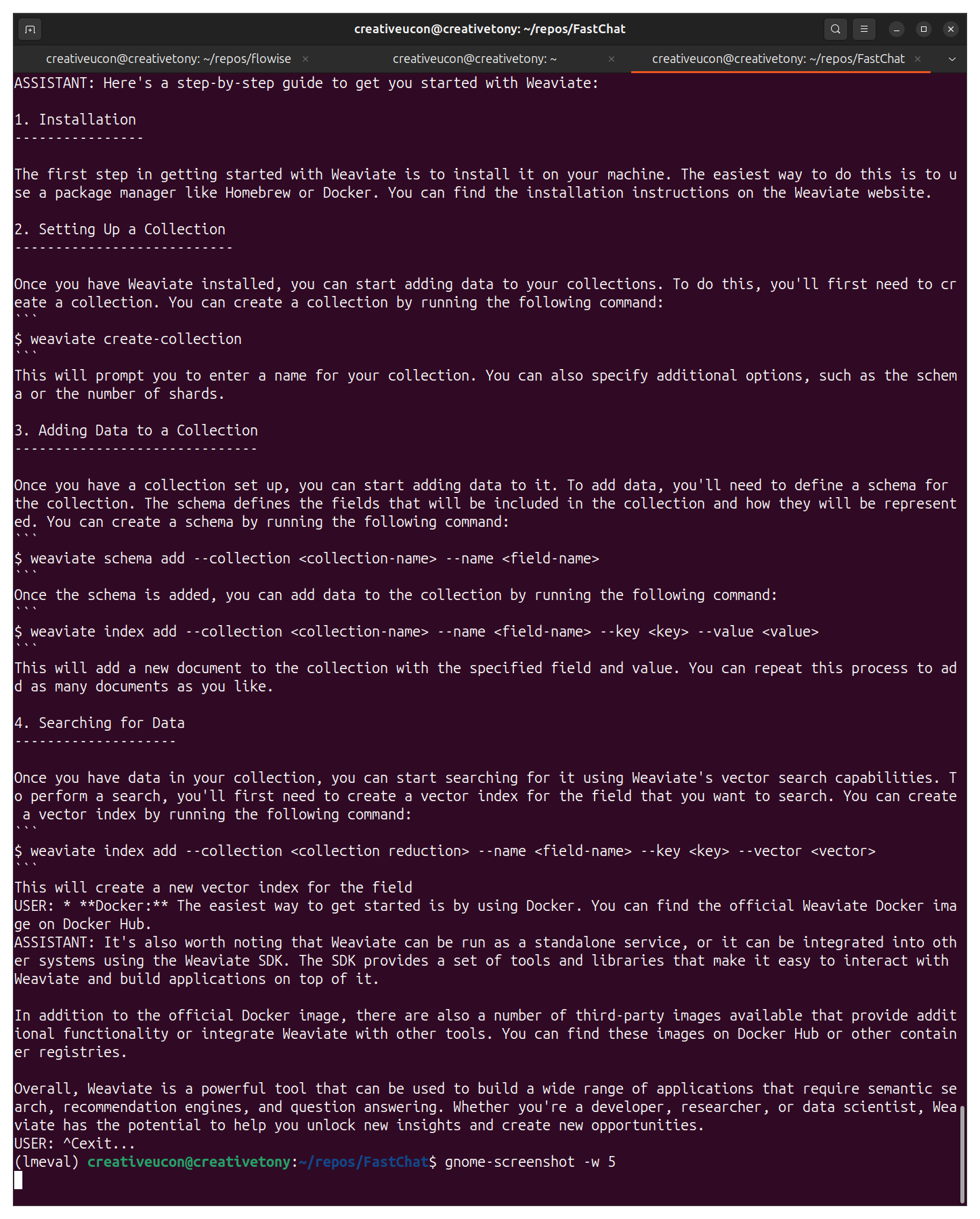
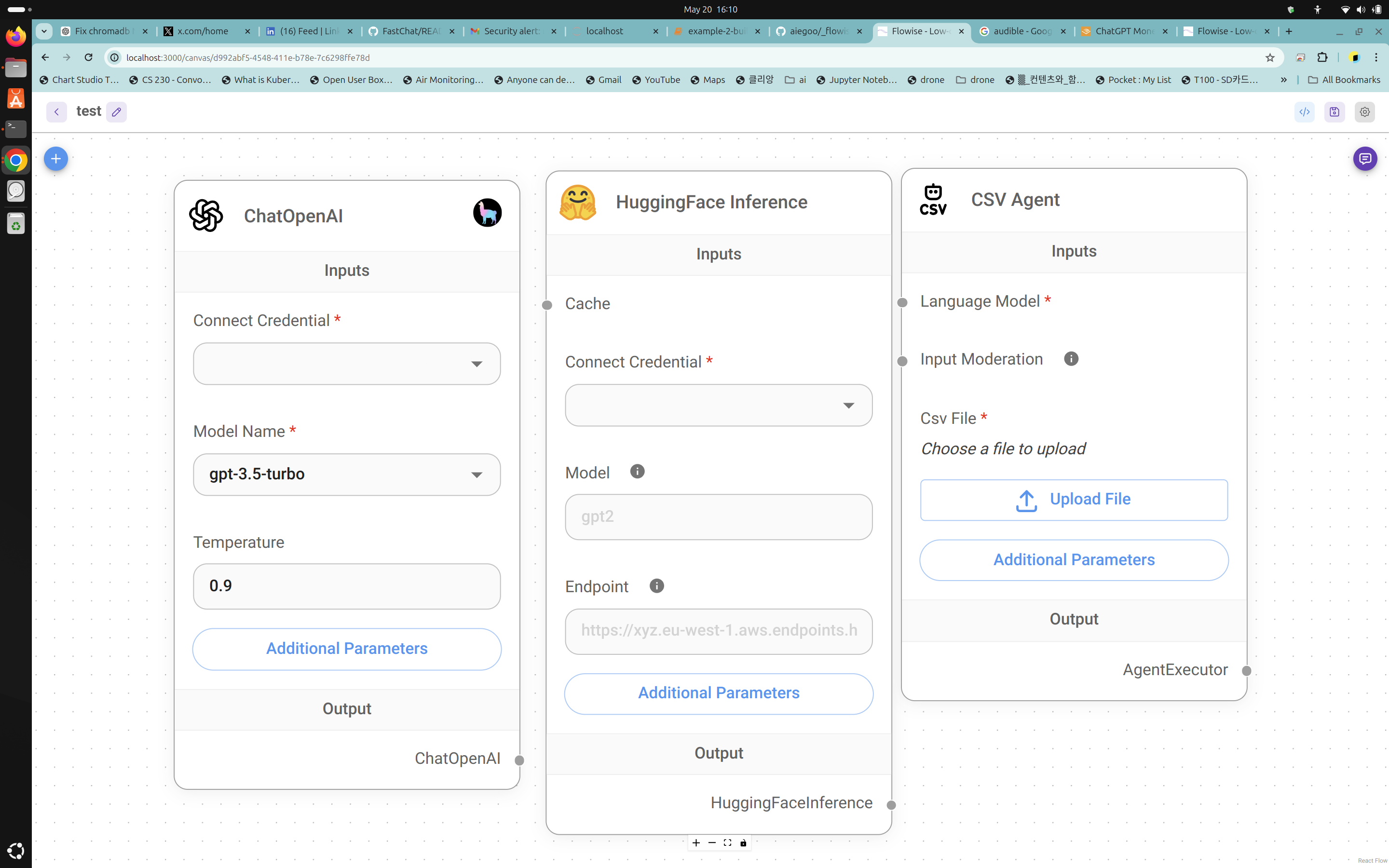
- LLM Model Learning Curves:
- Detailed analysis and experimentation with different LLM models to understand t heir learning curves and performance metrics.
- Utilized FastChat CLI and Flowise UI for model training and evaluation.
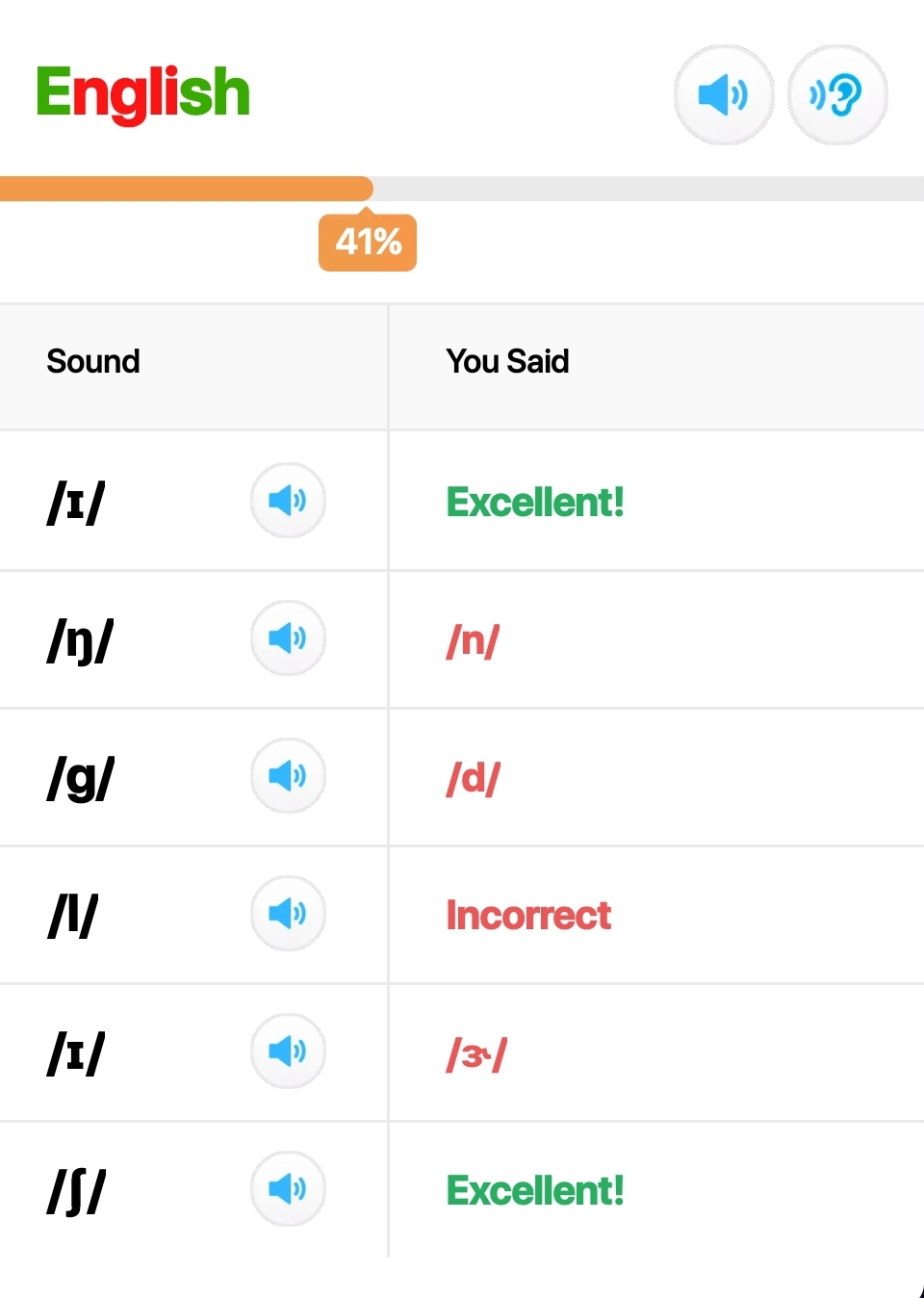
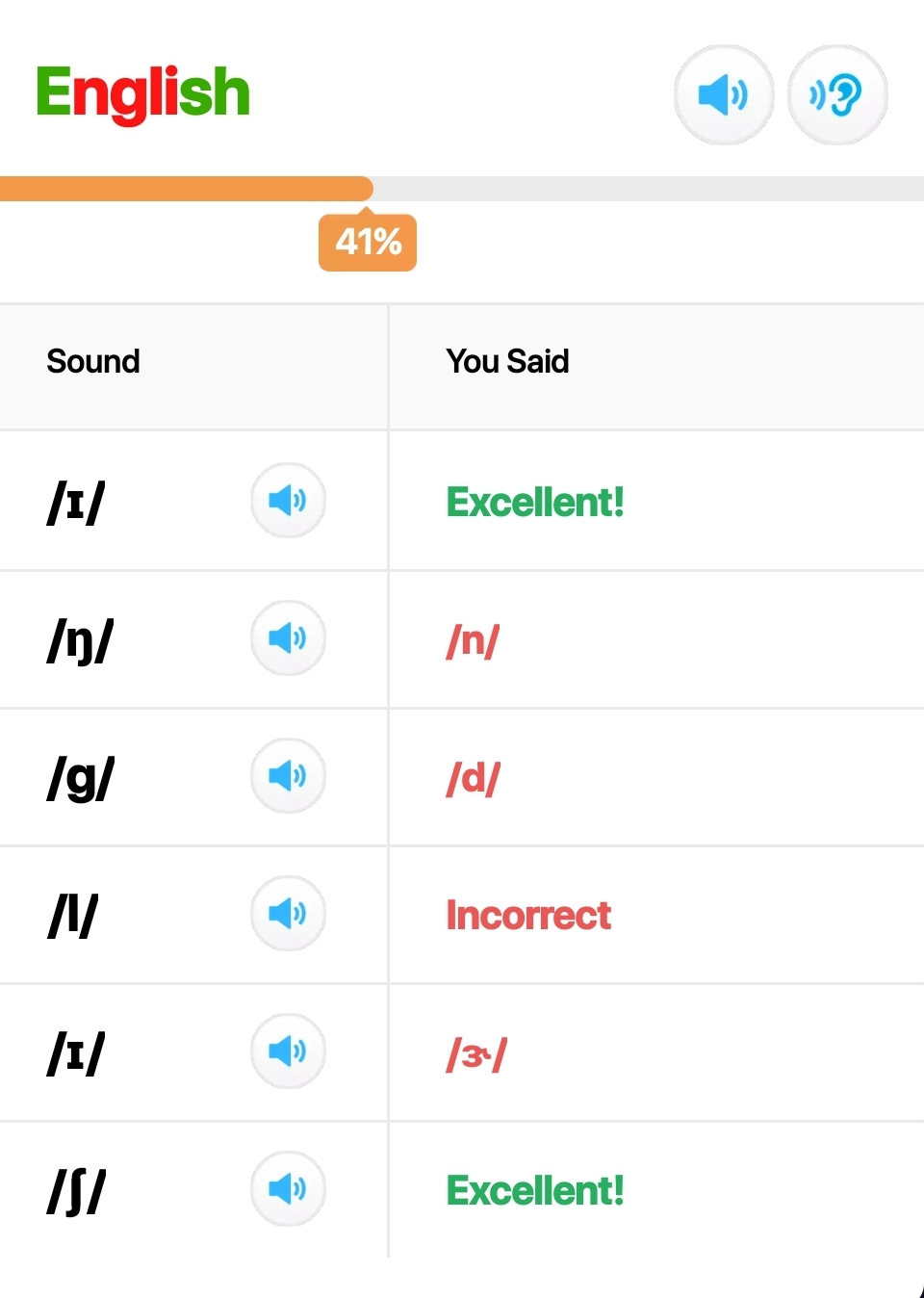
- Pronunciation Coach Project:
- Development of a pronunciation coach application using edge ML techniques.
- The project aims to provide real-time feedback on pronunciation using embedded devices.
- Demonstration of the project’s functionality can be seen in the video below.
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
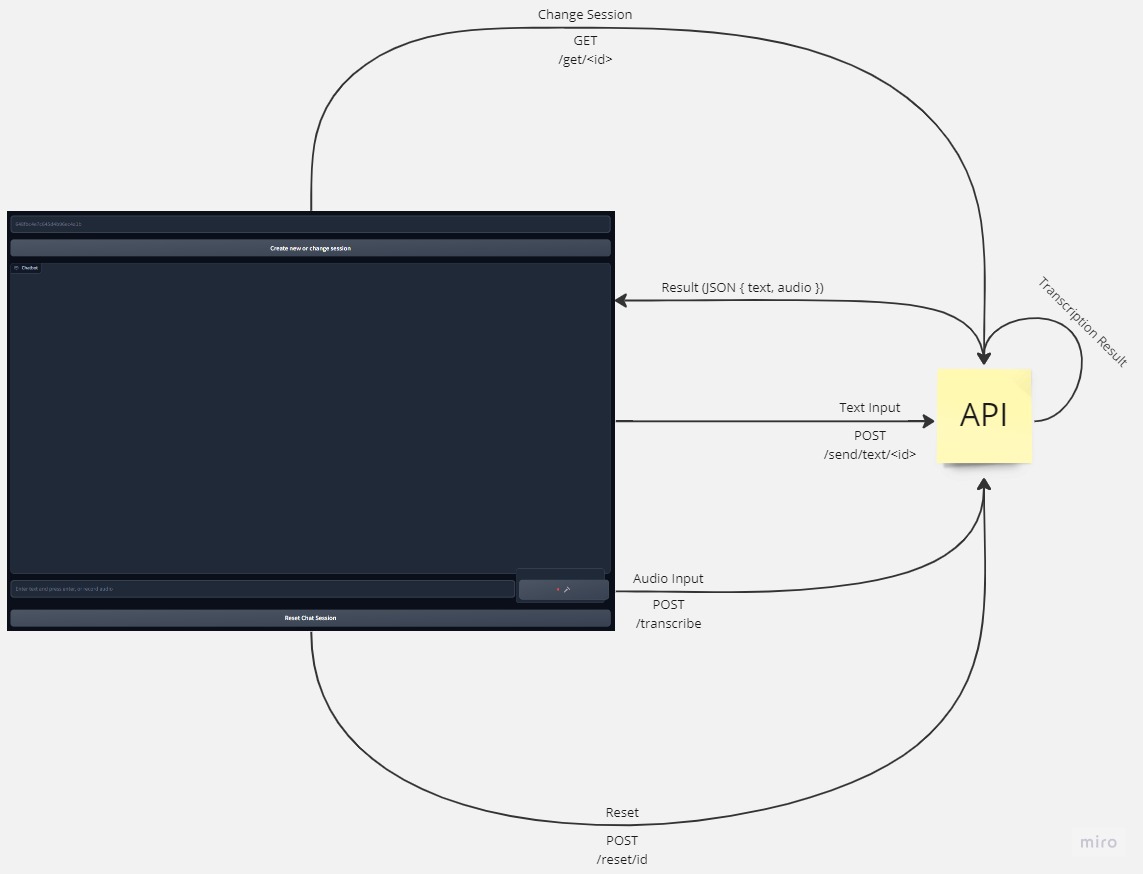
Deploy on Docker
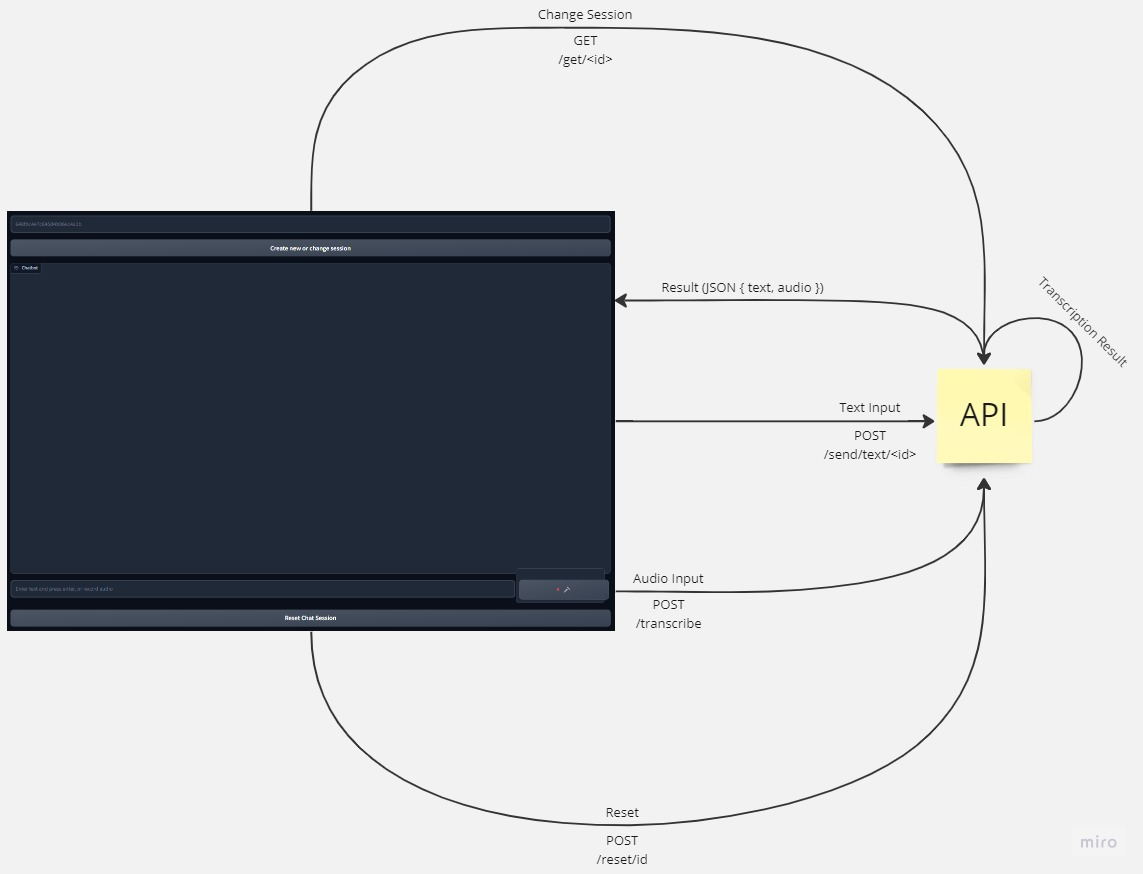
This document provides step-by-step instructions for deploying the API and the application. The process has two parts.
Part 1: Deployment of API
Step 1: Pull the Repository
git clone https://github.com/rifkybujana/Korean-Voice-QnA
Step 2: Install Requirements
cd Korean-Voice-QnA
pip install -r requirements-min.txt
Step 3: Create Docker Network
docker network create mongo-network
Step 4: Run MongoDB Docker Image
docker run -d --network mongo-network --name mongodb -p 27017:27017 mongo
Step 5: Convert New Model
ct2-transformers-converter --model openai/whisper-large-v2 --output_dir model --copy_files tokenizer.json --quantization float16
Step 6: Add your OpenAI API key
cp .env.example .env
Edit OPENAI_API_KEY inside .env.
Step 7: Build Docker Image
docker build -t api-image .
Step 8: Run Docker Image
docker run -it --rm --gpus all --name api-container -p 5000:5000 --network mongo-network api-image
The API is now available at http://localhost:5000 and http://<public_ip>:5000.
Part 2: Deployment of Application (outside Hugging Face Space)
Step 1: Pull Hugging Face Space
git clone https://huggingface.co/spaces/aiegoo/whisper-chatbot-ko
Step 2: Update public API endpoint
Open app.py and set PUBLIC_API_ENDPOINT to your API URL.
Step 3: Run the Application
cd whisper-chatbot-ko
python app.py
Notes:
- On Linux, allow the port: ufw allow 7860
- Enable SSL to access the user microphone.
- To run in background, use screen.
The following wiki, pages and posts are tagged with
| Title | Type | Excerpt |
|---|
{# nothing on index to avoid visible raw text #}