- Introduction to Bebop Autonomy Project
- Hardware Modifications and UART Access
- ROS Integration and Autonomous Flight
- Advanced Features
- Hardware Specifications and Performance
- Installation and Setup
- Conclusion
- References and Further Reading
Introduction to Bebop Autonomy Project
Repository: bebop_autonomy
This project provides a comprehensive ROS driver for Parrot Bebop Drones 1.0 & 2.0, enabling autonomous flight capabilities and advanced telemetry access through hardware modifications.
Hardware Modifications and UART Access
Opening the Bebop Drone
The first step in gaining full control over the Bebop involves carefully disassembling the drone to access internal components.
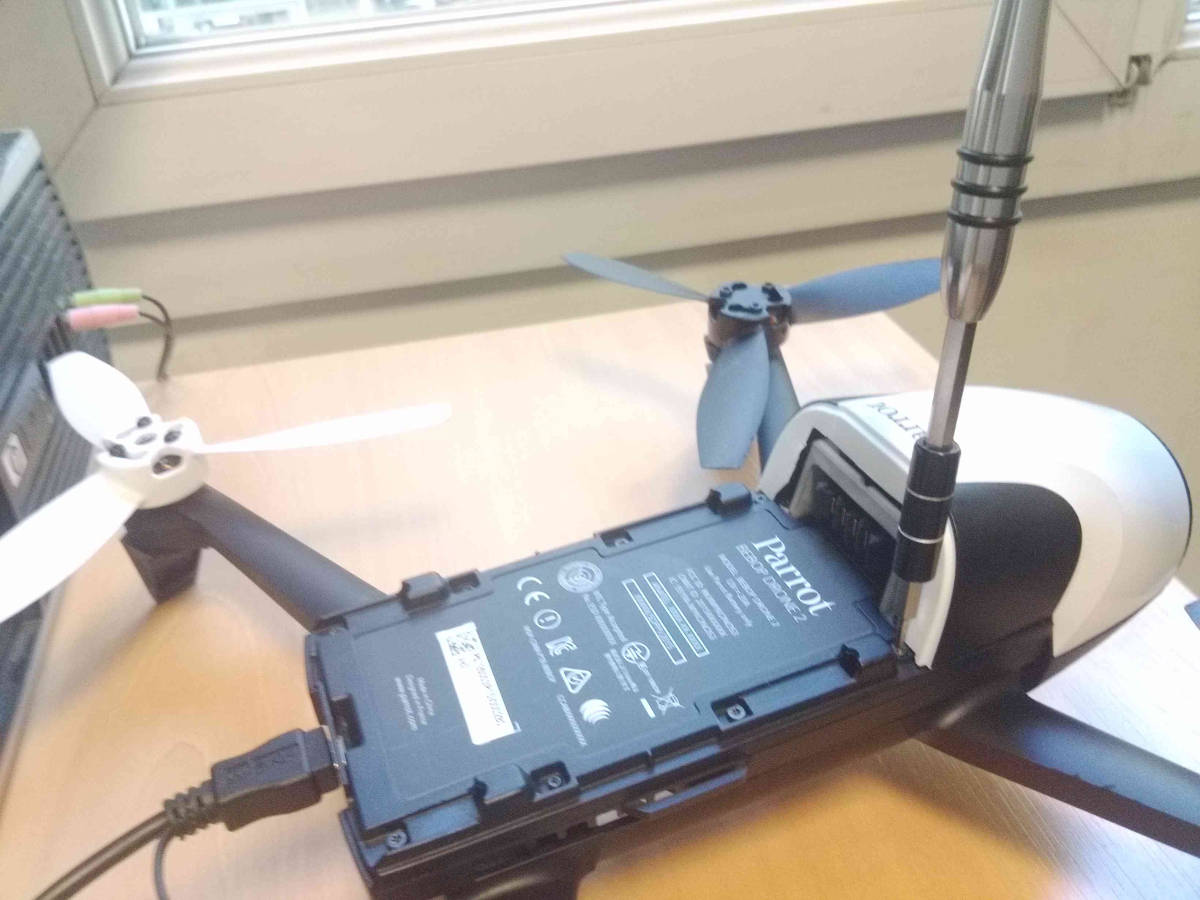 Carefully removing the screws to access internal components
Carefully removing the screws to access internal components
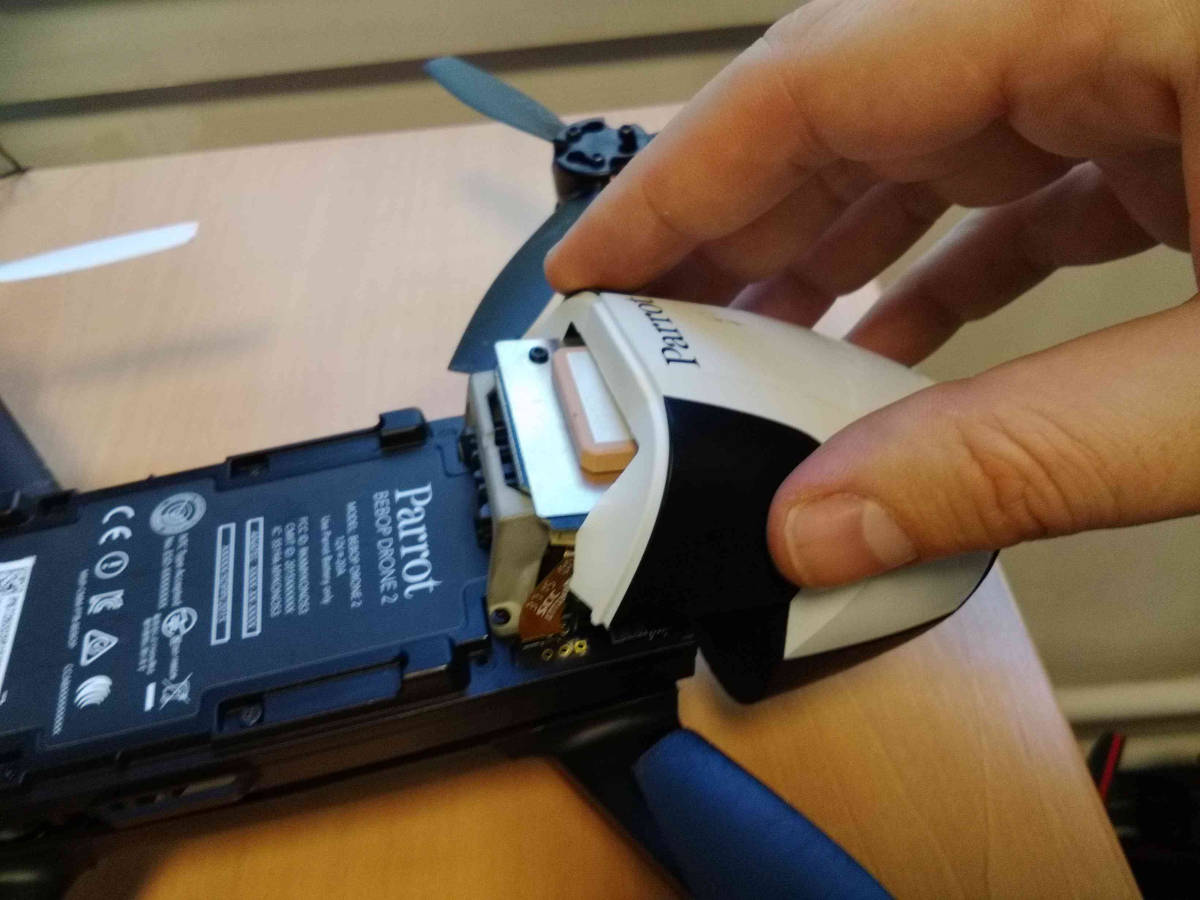 Removing the neck assembly for deeper hardware access
Removing the neck assembly for deeper hardware access
UART Connection Setup
To enable advanced debugging and low-level control, we establish a UART connection to the drone’s main processor.
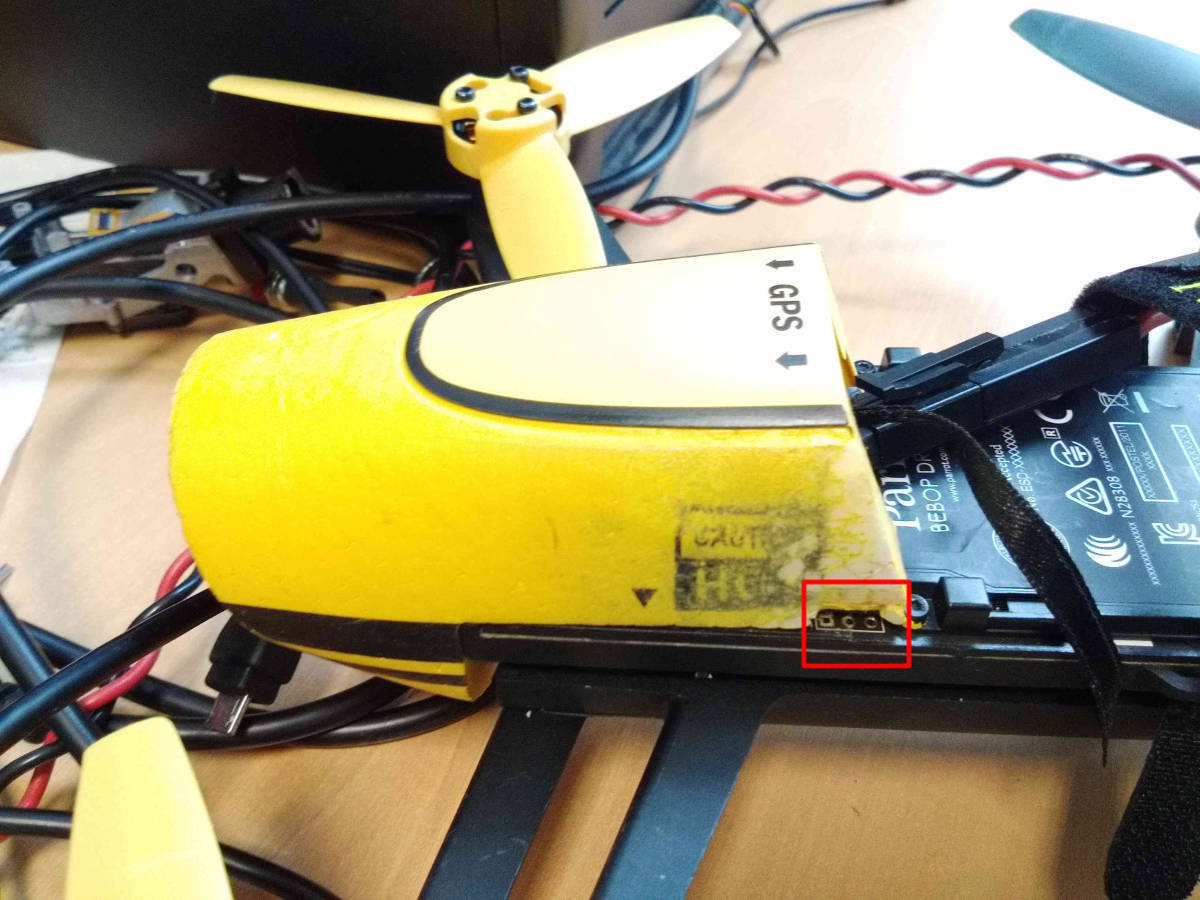 Location of the UART port on the Bebop mainboard
Location of the UART port on the Bebop mainboard
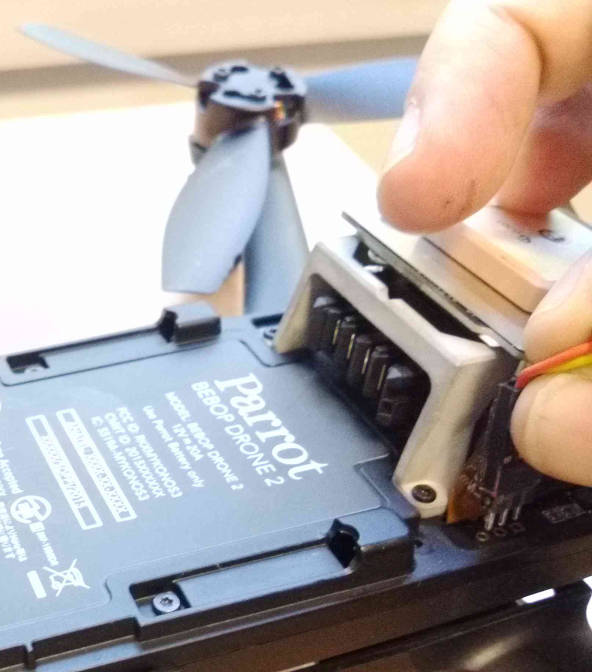 Proper UART connection setup for telemetry access
Proper UART connection setup for telemetry access
Required Hardware for UART Connection
- Single Pin Header Connectors: For creating reliable connections
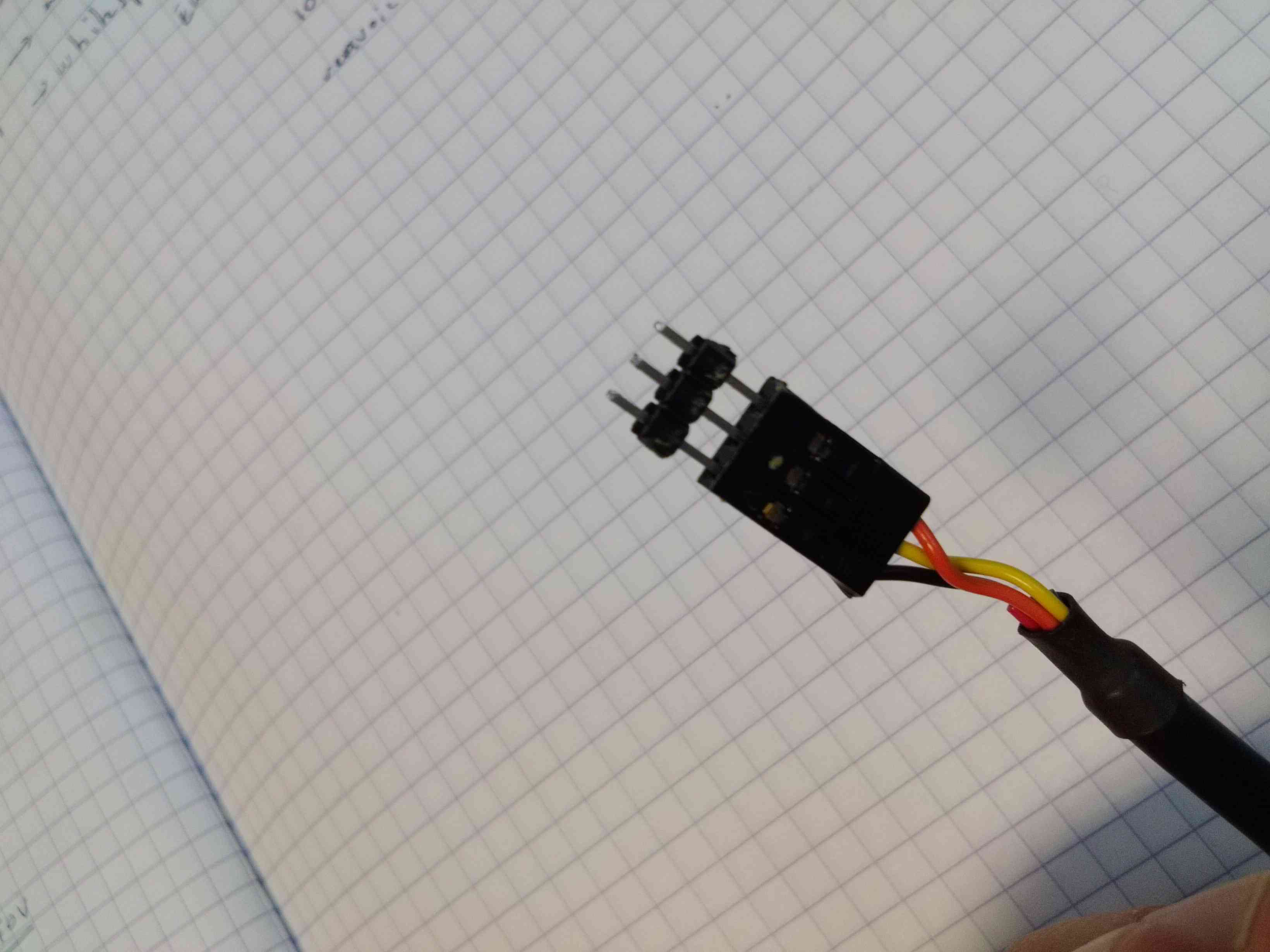 Single pin header connectors for UART interface
Single pin header connectors for UART interface
UART Connection Specifications
# UART Configuration
Baud Rate: 115200
Data Bits: 8
Stop Bits: 1
Parity: None
Flow Control: None
# Connection Pinout
Pin 1: GND (Ground)
Pin 2: RX (Receive - connect to TX of USB-Serial adapter)
Pin 3: TX (Transmit - connect to RX of USB-Serial adapter)
Pin 4: 3.3V (Power - do not connect to external power)
Complete Connection Setup
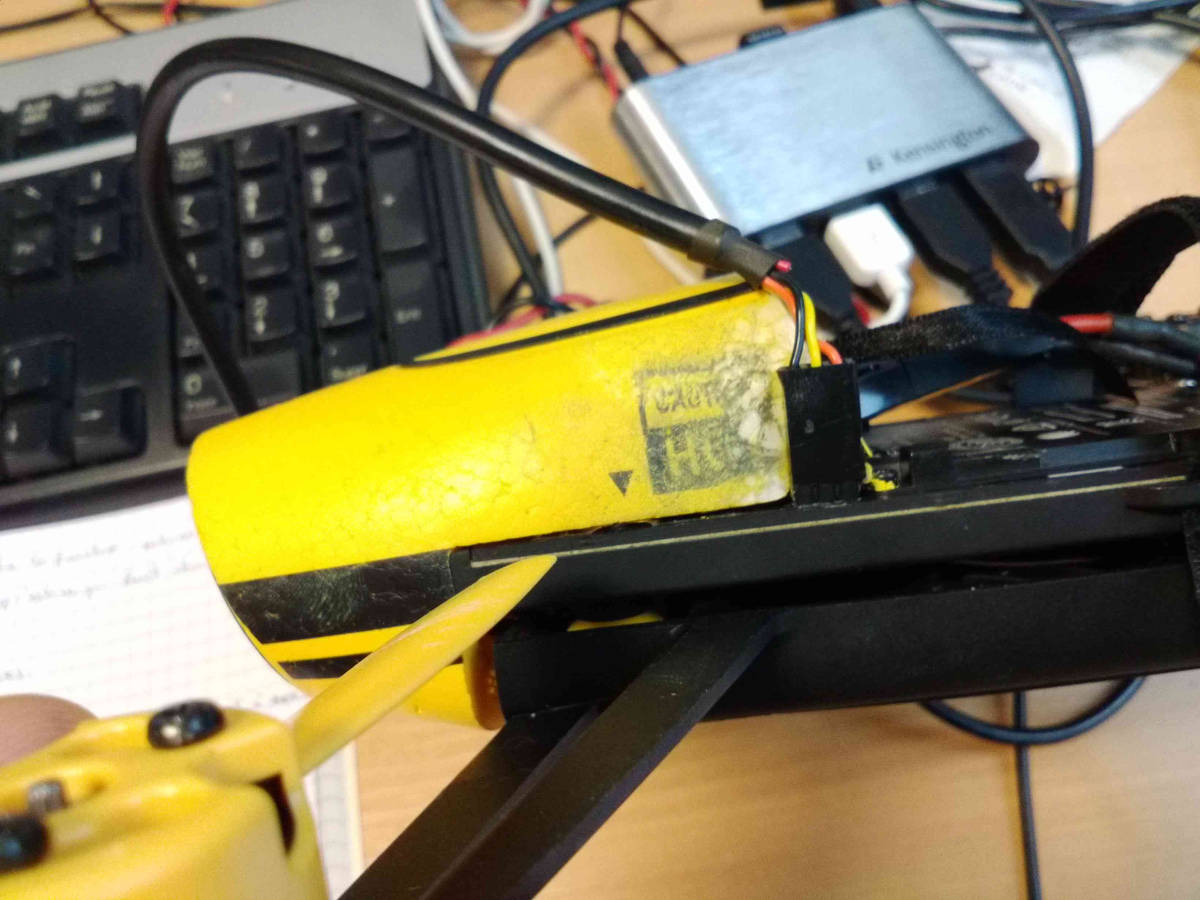 Complete connection setup showing all interfaces
Complete connection setup showing all interfaces
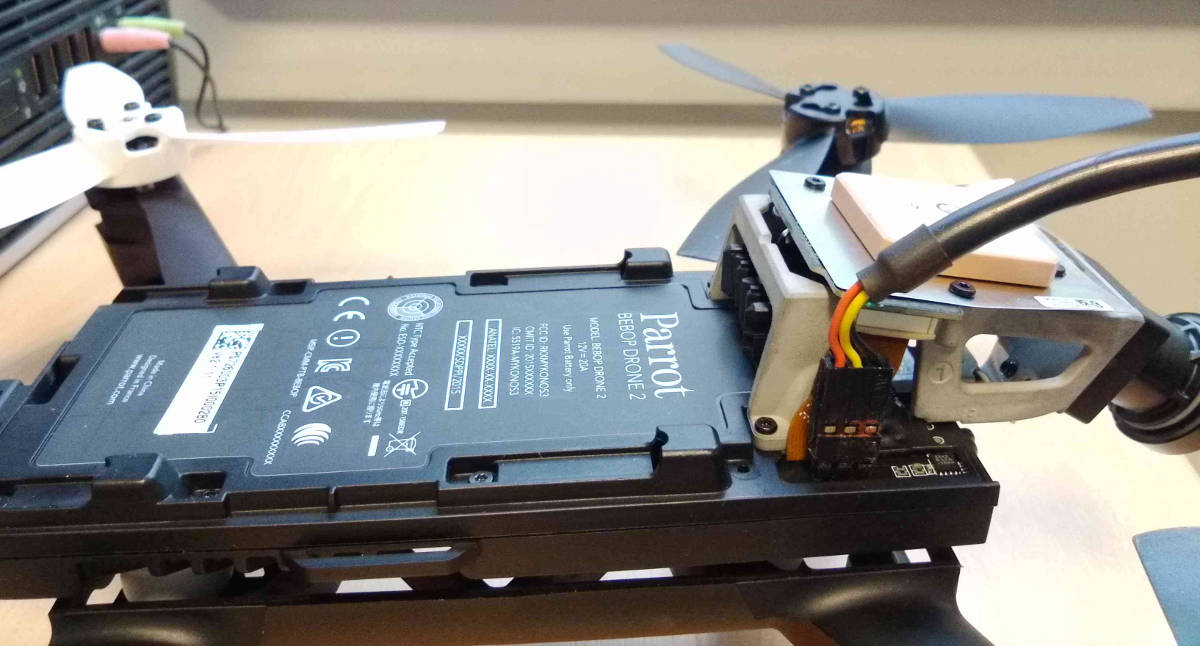 Detailed view of the connection assembly
Detailed view of the connection assembly
ROS Integration and Autonomous Flight
ROS Driver Architecture
The Bebop autonomy system provides a comprehensive ROS interface for flight control and sensor data access.
#!/usr/bin/env python
"""
Bebop Autonomous Flight Controller
Integrates with ROS for high-level mission planning
"""
import rospy
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image, Imu
from std_msgs.msg import Empty, Bool
from bebop_msgs.msg import Ardrone3PilotingStateFlightStateChanged
class BebopAutonomousController:
def __init__(self):
rospy.init_node('bebop_autonomous_controller')
# Publishers for flight control
self.cmd_vel_pub = rospy.Publisher('/bebop/cmd_vel', Twist, queue_size=1)
self.takeoff_pub = rospy.Publisher('/bebop/takeoff', Empty, queue_size=1)
self.land_pub = rospy.Publisher('/bebop/land', Empty, queue_size=1)
# Subscribers for sensor data
rospy.Subscriber('/bebop/image_raw', Image, self.image_callback)
rospy.Subscriber('/bebop/imu', Imu, self.imu_callback)
rospy.Subscriber('/bebop/states/flight',
Ardrone3PilotingStateFlightStateChanged,
self.flight_state_callback)
# Flight state variables
self.current_flight_state = 0 # 0=landed, 1=takeoff, 2=hovering, etc.
self.autonomous_mode = False
self.mission_waypoints = []
self.current_waypoint_index = 0
rospy.loginfo("Bebop Autonomous Controller initialized")
def image_callback(self, msg):
"""Process camera feed for computer vision"""
# Convert ROS image to OpenCV format
cv_image = self.bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(msg, "bgr8")
# Process image for navigation
navigation_command = self.process_vision_navigation(cv_image)
if self.autonomous_mode:
self.execute_navigation_command(navigation_command)
def imu_callback(self, msg):
"""Process IMU data for attitude control"""
self.current_orientation = msg.orientation
self.current_angular_velocity = msg.angular_velocity
self.current_linear_acceleration = msg.linear_acceleration
# Update flight controller with IMU data
self.update_attitude_controller()
def flight_state_callback(self, msg):
"""Monitor flight state changes"""
self.current_flight_state = msg.state
rospy.loginfo(f"Flight state changed to: {msg.state}")
if msg.state == 2 and self.autonomous_mode: # Hovering
self.start_autonomous_mission()
def autonomous_takeoff(self):
"""Initiate autonomous takeoff sequence"""
rospy.loginfo("Starting autonomous takeoff")
takeoff_msg = Empty()
self.takeoff_pub.publish(takeoff_msg)
self.autonomous_mode = True
def autonomous_land(self):
"""Initiate autonomous landing sequence"""
rospy.loginfo("Starting autonomous landing")
land_msg = Empty()
self.land_pub.publish(land_msg)
self.autonomous_mode = False
def execute_waypoint_mission(self, waypoints):
"""Execute a series of GPS waypoints"""
self.mission_waypoints = waypoints
self.current_waypoint_index = 0
if self.current_flight_state == 2: # Already hovering
self.navigate_to_next_waypoint()
def navigate_to_next_waypoint(self):
"""Navigate to the next waypoint in the mission"""
if self.current_waypoint_index >= len(self.mission_waypoints):
rospy.loginfo("Mission completed, landing")
self.autonomous_land()
return
target_waypoint = self.mission_waypoints[self.current_waypoint_index]
# Calculate navigation command to reach waypoint
cmd_vel = self.calculate_waypoint_navigation(target_waypoint)
self.cmd_vel_pub.publish(cmd_vel)
rospy.loginfo(f"Navigating to waypoint {self.current_waypoint_index + 1}")
Computer Vision Integration
The system integrates computer vision for obstacle avoidance and target tracking:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from cv_bridge import CvBridge
class BebopVisionSystem:
def __init__(self):
self.bridge = CvBridge()
self.obstacle_detector = self.load_obstacle_detection_model()
self.target_tracker = self.load_target_tracking_model()
def process_vision_navigation(self, cv_image):
"""Process camera feed for autonomous navigation"""
# Obstacle detection
obstacles = self.detect_obstacles(cv_image)
# Target tracking (if mission requires)
targets = self.track_targets(cv_image)
# Generate navigation command
navigation_cmd = self.generate_navigation_command(obstacles, targets)
return navigation_cmd
def detect_obstacles(self, image):
"""Detect obstacles in the camera feed"""
# Convert to HSV for better color detection
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
# Edge detection for obstacle boundaries
edges = cv2.Canny(image, 50, 150)
# Contour detection for object identification
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(edges, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
obstacles = []
for contour in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
if area > 1000: # Filter small objects
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contour)
obstacles.append({
'bbox': (x, y, w, h),
'area': area,
'distance': self.estimate_distance(w, h)
})
return obstacles
def estimate_distance(self, width, height):
"""Estimate distance to object based on bounding box size"""
# Simplified distance estimation
# In practice, would use stereo vision or known object sizes
focal_length = 500 # Camera focal length in pixels
known_object_width = 0.3 # meters
if width > 0:
distance = (known_object_width * focal_length) / width
return distance
return float('inf')
def generate_navigation_command(self, obstacles, targets):
"""Generate navigation command based on vision analysis"""
cmd_vel = Twist()
# Default forward motion
cmd_vel.linear.x = 0.2 # 0.2 m/s forward
# Obstacle avoidance
for obstacle in obstacles:
if obstacle['distance'] < 2.0: # Too close
# Turn away from obstacle
bbox = obstacle['bbox']
image_center = 320 # Assuming 640px width
obstacle_center = bbox[0] + bbox[2] / 2
if obstacle_center < image_center:
cmd_vel.angular.z = -0.3 # Turn right
else:
cmd_vel.angular.z = 0.3 # Turn left
cmd_vel.linear.x = 0.0 # Stop forward motion
break
return cmd_vel
Flight Mission Planning
Advanced mission planning capabilities for autonomous operations:
class BebopMissionPlanner:
def __init__(self):
self.flight_controller = BebopAutonomousController()
self.gps_waypoints = []
self.mission_type = None
def plan_area_survey_mission(self, area_bounds, altitude=10.0):
"""Plan a systematic area survey mission"""
# Generate grid pattern waypoints
min_lat, min_lon = area_bounds['southwest']
max_lat, max_lon = area_bounds['northeast']
# Calculate survey pattern
spacing = 0.0001 # Approximately 10m spacing
waypoints = []
lat = min_lat
direction = 1 # 1 for east, -1 for west
while lat <= max_lat:
if direction == 1:
lon_start, lon_end = min_lon, max_lon
else:
lon_start, lon_end = max_lon, min_lon
waypoints.append({
'lat': lat,
'lon': lon_start,
'alt': altitude,
'action': 'navigate'
})
waypoints.append({
'lat': lat,
'lon': lon_end,
'alt': altitude,
'action': 'navigate'
})
lat += spacing
direction *= -1 # Alternate direction for efficient coverage
return waypoints
def plan_inspection_mission(self, target_locations):
"""Plan an inspection mission for specific targets"""
waypoints = []
for i, target in enumerate(target_locations):
# Approach waypoint
waypoints.append({
'lat': target['lat'],
'lon': target['lon'],
'alt': target['alt'] + 5.0, # 5m above target
'action': 'navigate'
})
# Inspection hover point
waypoints.append({
'lat': target['lat'],
'lon': target['lon'],
'alt': target['alt'] + 2.0, # 2m above target
'action': 'hover_inspect',
'duration': 30.0 # 30 seconds inspection
})
# Circle around target for 360° view
circle_waypoints = self.generate_circle_waypoints(
target['lat'], target['lon'], target['alt'] + 3.0, radius=5.0
)
waypoints.extend(circle_waypoints)
return waypoints
def execute_mission(self, waypoints):
"""Execute the planned mission"""
rospy.loginfo(f"Starting mission with {len(waypoints)} waypoints")
# Takeoff first
self.flight_controller.autonomous_takeoff()
# Wait for takeoff completion
rate = rospy.Rate(10) # 10 Hz
while self.flight_controller.current_flight_state != 2: # Not hovering
rate.sleep()
# Execute waypoint mission
self.flight_controller.execute_waypoint_mission(waypoints)
Advanced Features
Real-time Telemetry and Logging
class BebopTelemetryLogger:
def __init__(self):
self.telemetry_data = {
'timestamp': [],
'position': [],
'attitude': [],
'velocity': [],
'battery_level': [],
'flight_state': []
}
def log_telemetry(self):
"""Continuously log flight telemetry data"""
rospy.Subscriber('/bebop/odom', Odometry, self.odom_callback)
rospy.Subscriber('/bebop/battery', BatteryState, self.battery_callback)
def save_flight_log(self, filename):
"""Save telemetry data to file"""
import json
with open(filename, 'w') as f:
json.dump(self.telemetry_data, f, indent=2)
Emergency Safety Features
class BebopSafetySystem:
def __init__(self):
self.emergency_land_pub = rospy.Publisher('/bebop/emergency', Empty, queue_size=1)
self.safety_checks_enabled = True
def monitor_safety_conditions(self):
"""Continuously monitor safety conditions"""
# Battery level check
if self.battery_level < 20.0:
rospy.logwarn("Low battery detected, initiating emergency landing")
self.emergency_land()
# GPS signal check
if not self.gps_fix_available:
rospy.logwarn("GPS signal lost, switching to manual control")
self.disable_autonomous_mode()
# Wind speed check
if self.wind_speed > 10.0: # m/s
rospy.logwarn("High wind detected, landing for safety")
self.emergency_land()
def emergency_land(self):
"""Execute emergency landing procedure"""
emergency_msg = Empty()
self.emergency_land_pub.publish(emergency_msg)
Hardware Specifications and Performance
Bebop Drone Specifications
- Flight Time: 11 minutes
- Camera: 1080p HD with 3-axis stabilization
- Range: 300m with smartphone, 2km with SkyController
- Max Speed: 13 m/s horizontal, 6 m/s vertical
- Weight: 400g
- Sensors: Accelerometer, Gyroscope, Magnetometer, GPS, Barometer
Performance Metrics
- Control Latency: <50ms via WiFi
- UART Communication: 115200 baud
- Video Streaming: 1080p at 30fps
- Autonomous Navigation Accuracy: ±1m with GPS
- Obstacle Avoidance Range: 2-10m depending on conditions
Installation and Setup
ROS Package Installation
# Create catkin workspace
mkdir -p ~/bebop_ws/src
cd ~/bebop_ws/src
# Clone bebop_autonomy repository
git clone https://github.com/aiegoo/bebop_autonomy.git
# Install dependencies
cd ~/bebop_ws
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
# Build the package
catkin_make
# Source the workspace
echo "source ~/bebop_ws/devel/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
Hardware Setup Requirements
- USB-to-UART adapter (3.3V compatible)
- Single pin header connectors
- Small Phillips head screwdriver
- Anti-static wrist strap (recommended)
- Multimeter for testing connections
Network Configuration
# Connect to Bebop WiFi network
sudo nmcli dev wifi connect "Bebop2-######" password "bebop2password"
# Verify connection
ping 192.168.42.1
# Launch ROS driver
roslaunch bebop_driver bebop_node.launch
Conclusion
The Bebop Autonomy project demonstrates comprehensive drone modification and autonomous flight control implementation. Through hardware modifications including UART access and ROS integration, the system enables:
- Advanced Telemetry: Direct access to low-level flight data
- Autonomous Navigation: GPS waypoint missions and computer vision guidance
- Safety Systems: Emergency procedures and condition monitoring
- Extensible Framework: Easy integration of additional sensors and capabilities
The project serves as a foundation for advanced drone research and development, providing both hardware access and software frameworks for autonomous flight applications.
References and Further Reading
{# nothing on index to avoid visible raw text #}